Brain-Computer Interfaces for Treatment of Focal Dystonia
- PMID: 35947366
- PMCID: PMC9474652
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.29178
Brain-Computer Interfaces for Treatment of Focal Dystonia
Abstract
Task-specificity in isolated focal dystonias is a powerful feature that may successfully be targeted with therapeutic brain-computer interfaces. While performing a symptomatic task, the patient actively modulates momentary brain activity (disorder signature) to match activity during an asymptomatic task (target signature), which is expected to translate into symptom reduction.
© 2022 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

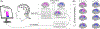
References
-
- Conte A, Rocchi L, Latorre A, Belvisi D, Rothwell JC, Berardelli A. Ten-year reflections on the neurophysiological abnormalities of focal dystonias in humans. Mov Disord 2019;34(11):1616–1628. - PubMed
-
- Balint B, Mencacci NE, Valente EM, et al. Dystonia. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2018;4(1):25. - PubMed
-
- Vidailhet M, Jutras M-F, Roze E, Grabli D. Deep brain stimulation for dystonia. Handb Clin Neurol 2013;116:167–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

