Bee venom-loaded EGFR-targeting peptide-coupled chitosan nanoparticles for effective therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting EGFR-mediated MEK/ERK pathway
- PMID: 35947632
- PMCID: PMC9365195
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272776
Bee venom-loaded EGFR-targeting peptide-coupled chitosan nanoparticles for effective therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting EGFR-mediated MEK/ERK pathway
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Bee venom-loaded EGFR-targeting peptide-coupled chitosan nanoparticles for effective therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting EGFR-mediated MEK/ERK pathway.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 23;18(6):e0287805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287805. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37352224 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
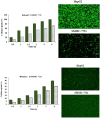
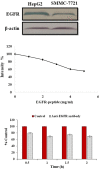
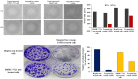
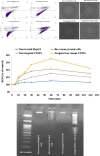
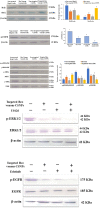
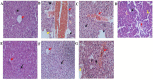
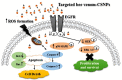
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the world's most risky diseases due to the lack of clear and cost-effective therapeutic targets. Currently, the toxicity of conventional chemotherapeutic medications and the development of multidrug resistance is driving research into targeted therapies. The nano-biomedical field's potential for developing an effective therapeutic nano-sized drug delivery system is viewed as a significant pharmaceutical trend for the encapsulation and release of numerous anticancer therapies. In this regard, current research is centered on the creation of biodegradable chitosan nanoparticles (CSNPs) for the selective and sustained release of bee venom into liver cancer cells. Furthermore, surface modification with polyethylene glycol (PEG) and GE11 peptide-conjugated bee venom-CSNPs allows for the targeting of EGFR-overexpressed liver cancer cells. A series of in vitro and in vivo cellular analyses were used to investigate the antitumor effects and mechanisms of targeted bee venom-CSNPs. Targeted bee venom-CSNPs, in particular, were found to have higher cytotoxicity against HepG2 cells than SMMC-7721 cells, as well as stronger cellular uptake and a substantial reduction in cell migration, leading to improved cancer suppression. It also promotes cancer cell death in EGFR overexpressed HepG2 cells by boosting reactive oxygen species, activating mitochondria-dependent pathways, inhibiting EGFR-stimulated MEK/ERK pathway, and elevating p38-MAPK in comparison to native bee venom. In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)-induced mice, it has anti-cancer properties against tumor tissue. It also improved liver function and architecture without causing any noticeable toxic side effects, as well as inhibiting tumor growth by activating the apoptotic pathway. The design of this cancer-targeted nanoparticle establishes GE11-bee venom-CSNPs as a potential chemotherapeutic treatment for EGFR over-expressed malignancies. Finally, our work elucidates the molecular mechanism underlying the anticancer selectivity of targeted bee venom-CSNPs and outlines therapeutic strategies to target liver cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

