Disruption of the circadian clock drives Apc loss of heterozygosity to accelerate colorectal cancer
- PMID: 35947664
- PMCID: PMC9365282
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abo2389
Disruption of the circadian clock drives Apc loss of heterozygosity to accelerate colorectal cancer
Abstract
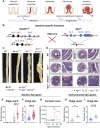
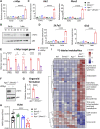
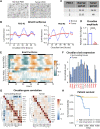
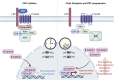
An alarming rise in young onset colorectal cancer (CRC) has been reported; however, the underlying molecular mechanism remains undefined. Suspected risk factors of young onset CRC include environmental aspects, such as lifestyle and dietary factors, which are known to affect the circadian clock. We find that both genetic disruption and environmental disruption of the circadian clock accelerate Apc-driven CRC pathogenesis in vivo. Using an intestinal organoid model, we demonstrate that clock disruption promotes transformation by driving Apc loss of heterozygosity, which hyperactivates Wnt signaling. This up-regulates c-Myc, a known Wnt target, which drives heightened glycolytic metabolism. Using patient-derived organoids, we show that circadian rhythms are lost in human tumors. Last, we identify that variance between core clock and Wnt pathway genes significantly predicts the survival of patients with CRC. Overall, our findings demonstrate a previously unidentified mechanistic link between clock disruption and CRC, which has important implications for young onset cancer prevention.
Figures



References
-
- Nusse R., Clevers H., Wnt/β-Catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell 169, 985–999 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Moser A. R., Pitot H. C., Dove W. F., A dominant mutation that predisposes to multiple intestinal neoplasia in the mouse. Science 247, 322–324 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Morin P. J., Sparks A. B., Korinek V., Barker N., Clevers H., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W., Activation of β-catenin-Tcf signaling in colon cancer by mutations in β-catenin or APC. Science 275, 1787–1790 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Korinek V., Barker N., Morin P. J., van Wichen D., de Weger R., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B., Clevers H., Constitutive transcriptional activation by a beta-catenin-Tcf complex in APC−/− colon carcinoma. Science 275, 1784–1787 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Rubinfeld B., Souza B., Albert I., Müller O., Chamberlain S. H., Masiarz F. R., Munemitsu S., Polakis P., Association of the APC gene product with β-catenin. Science 262, 1731–1734 (1993). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

