Medications for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 35948391
- PMCID: PMC9724821
- DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0036-2022
Medications for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: There is no consensus on the most effective treatments of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Our objective was to compare effects of medications for PAH.
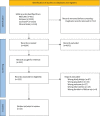
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, Embase, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials and Clinicaltrials.gov from inception to December 2021. We performed a frequentist random-effects network meta-analysis on all included trials. We rated the certainty of the evidence using the Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation approach.
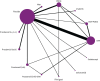
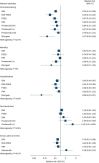
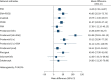
Results: We included 53 randomised controlled trials with 10 670 patients. Combination therapy with endothelin receptor antagonist (ERA) plus phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (PDE5i) reduced clinical worsening (120.7 fewer events per 1000, 95% CI 136.8-93.4 fewer; high certainty) and was superior to either ERA or PDE5i alone, both of which reduced clinical worsening, as did riociguat monotherapy (all high certainty). PDE5i (24.9 fewer deaths per 1000, 95% CI 35.2 fewer to 2.1 more); intravenous/subcutaneous prostanoids (18.3 fewer deaths per 1000, 95% CI 28.6 fewer deaths to 0) and riociguat (29.1 fewer deaths per 1000, 95% CI 38.6 fewer to 8.7 more) probably reduce mortality as compared to placebo (all moderate certainty). Combination therapy with ERA+PDE5i (49.9 m, 95% CI 25.9-73.8 m) and riociguat (49.5 m, 95% CI 17.3-81.7 m) probably increase 6-min walk distance as compared to placebo (moderate certainty).
Conclusion: Current PAH treatments improve clinically important outcomes, although the degree and certainty of benefit vary between treatments.
Copyright ©The authors 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: L. Mielniczuk discloses speaker fees/advisory boards/consulting fees from Janssen. She is a clinician scientist supported by Heart and Stroke Foundation. S. Mehta discloses speaker fees and consulting fees from Acceleron Pharmaceuticals and Janssen Pharmaceuticals, as well as institutional research support from Acceleron, Bellerophon, Gossamer Bio, Janssen, and United Therapeutics. The remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, et al. . 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J 2016; 37: 67–119. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehv317 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
