Establishment and assessment of rodent models of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ)
- PMID: 35948539
- PMCID: PMC9365764
- DOI: 10.1038/s41368-022-00182-4
Establishment and assessment of rodent models of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ)
Abstract
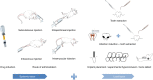
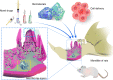
Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) is primarily associated with administering antiresorptive or antiangiogenic drugs. Despite significant research on MRONJ, its pathogenesis and effective treatments are still not fully understood. Animal models can be used to simulate the pathophysiological features of MRONJ, serving as standardized in vivo experimental platforms to explore the pathogenesis and therapies of MRONJ. Rodent models exhibit excellent effectiveness and high reproducibility in mimicking human MRONJ, but classical methods cannot achieve a complete replica of the pathogenesis of MRONJ. Modified rodent models have been reported with improvements for better mimicking of MRONJ onset in clinic. This review summarizes representative classical and modified rodent models of MRONJ created through various combinations of systemic drug induction and local stimulation and discusses their effectiveness and efficiency. Currently, there is a lack of a unified assessment system for MRONJ models, which hinders a standard definition of MRONJ-like lesions in rodents. Therefore, this review comprehensively summarizes assessment systems based on published peer-review articles, including new approaches in gross observation, histological assessments, radiographic assessments, and serological assessments. This review can serve as a reference for model establishment and evaluation in future preclinical studies on MRONJ.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Infection as an Important Factor in Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ).Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 May 9;57(5):463. doi: 10.3390/medicina57050463. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 34065104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw-like lesions in rodents: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.Gerodontology. 2019 Dec;36(4):313-324. doi: 10.1111/ger.12416. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Gerodontology. 2019. PMID: 31373407
-
Chronic Periodontal Infection and Not Iatrogenic Interference Is the Trigger of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: Insights from a Large Animal Study (PerioBRONJ Pig Model).Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 May 22;59(5):1000. doi: 10.3390/medicina59051000. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37241232 Free PMC article.
-
CT imaging features of antiresorptive agent-related osteonecrosis of the jaw/medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw.Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2018 May;47(4):20170323. doi: 10.1259/dmfr.20170323. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29365278 Free PMC article.
-
Rodents as an animal model for studying tooth extraction-related medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: assessment of outcomes.Arch Oral Biol. 2024 Mar;159:105875. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2023.105875. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Arch Oral Biol. 2024. PMID: 38160519 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of active oxygen gel on the clinical parameters of MRONJ.Saudi Dent J. 2024 Nov;36(11):1456-1458. doi: 10.1016/j.sdentj.2024.09.003. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Saudi Dent J. 2024. PMID: 39619723 Free PMC article.
-
Omega-3 attenuates the severity of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws in rats treated with zoledronate.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 26;20(3):e0320413. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320413. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40138277 Free PMC article.
-
The preventive effect of photocrosslinked Hep/GelMA hydrogel loaded with PRF on MRONJ.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Aug 29;24(1):1010. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04792-8. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39210345 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-adrenergic receptor antagonist propranolol prevents bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw by promoting osteogenesis.J Dent Sci. 2025 Jan;20(1):539-552. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2024.04.016. Epub 2024 May 4. J Dent Sci. 2025. PMID: 39873080 Free PMC article.
-
Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: A Cross-Sectional Survey among Urologists in Switzerland, Germany, and Austria.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 13;12(2):638. doi: 10.3390/jcm12020638. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36675567 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Poubel V, Silva CAB, Mezzomo LAM, De Luca Canto G, Rivero ERC. The risk of osteonecrosis on alveolar healing after tooth extraction and systemic administration of antiresorptive drugs in rodents: a systematic review. J. Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2018;46:245–256. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2017.11.008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

