Targeting the Retinoblastoma/E2F repressive complex by CDK4/6 inhibitors amplifies oncolytic potency of an oncolytic adenovirus
- PMID: 35948546
- PMCID: PMC9365808
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-32087-5
Targeting the Retinoblastoma/E2F repressive complex by CDK4/6 inhibitors amplifies oncolytic potency of an oncolytic adenovirus
Abstract
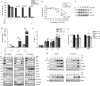
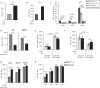
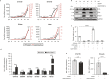
CDK4/6 inhibitors (CDK4/6i) and oncolytic viruses are promising therapeutic agents for the treatment of various cancers. As single agents, CDK4/6 inhibitors that are approved for the treatment of breast cancer in combination with endocrine therapy cause G1 cell cycle arrest, whereas adenoviruses induce progression into S-phase in infected cells as an integral part of the their life cycle. Both CDK4/6 inhibitors and adenovirus replication target the Retinoblastoma protein albeit for different purposes. Here we show that in combination CDK4/6 inhibitors potentiate the anti-tumor effect of the oncolytic adenovirus XVir-N-31 in bladder cancer and murine Ewing sarcoma xenograft models. This increase in oncolytic potency correlates with an increase in virus-producing cancer cells, enhanced viral genome replication, particle formation and consequently cancer cell killing. The molecular mechanism that regulates this response is fundamentally based on the reduction of Retinoblastoma protein expression levels by CDK4/6 inhibitors.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
P.S.H. is co-founder of XVir Therapeutics GmbH. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Chesney J, et al. Randomized, Open-Label Phase II Study evaluating the efficacy and safety of talimogene laherparepvec in combination with ipilimumab versus ipilimumab alone in patients with advanced, unresectable melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;36:1658–1667. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.73.7379. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

