Effectiveness of third vaccine dose for coronavirus disease 2019 during the Omicron variant pandemic: a prospective observational study in Japan
- PMID: 35948626
- PMCID: PMC9365759
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-17990-7
Effectiveness of third vaccine dose for coronavirus disease 2019 during the Omicron variant pandemic: a prospective observational study in Japan
Abstract
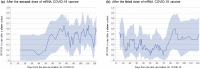
The administration of a third booster dose of messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) vaccines against coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has progressed worldwide. Since January 2022, Japan has faced a nationwide outbreak caused by the Omicron variant, which occurred simultaneously with the progression of mass vaccination with the third booster dose. Therefore, this study evaluated the effectiveness of the third dose of vaccine by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test using nasopharyngeal swab samples from adults aged ≥ 18 years tested after having close contact with COVID-19 cases between January and May 2022. Participants who completed only one dose were excluded from the study. Among the 928 enrolled participants, 139 had never been vaccinated, 609 had completed two doses, 180 had completed three doses before the swab test, and the overall RT-PCR test positivity rate in each group was 48.9%, 46.0%, and 32.2%, respectively. The vaccine effectiveness of the third dose to prevent infection after close contact was approximately 40% (95% confidence interval: 20-60%), which was the highest at 10-70 days after receiving the third dose. In conclusion, the effectiveness of the three-dose mRNA COVID-19 vaccine after close contact during the Omicron outbreak is approximately 40%.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines in Japan during the Nationwide Pandemic of the Delta Variant.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2022 May 13;257(1):1-6. doi: 10.1620/tjem.2022.J012. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 35354690
-
Effectiveness of a Third Dose of mRNA Vaccines Against COVID-19-Associated Emergency Department and Urgent Care Encounters and Hospitalizations Among Adults During Periods of Delta and Omicron Variant Predominance - VISION Network, 10 States, August 2021-January 2022.MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022 Jan 21;71(4):139-145. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7104e3. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022. PMID: 35085224 Free PMC article.
-
Waning 2-Dose and 3-Dose Effectiveness of mRNA Vaccines Against COVID-19-Associated Emergency Department and Urgent Care Encounters and Hospitalizations Among Adults During Periods of Delta and Omicron Variant Predominance - VISION Network, 10 States, August 2021-January 2022.MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022 Feb 18;71(7):255-263. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7107e2. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022. PMID: 35176007 Free PMC article.
-
The Vaccine Efficacy Against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Jul 13;10:940956. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.940956. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35910897 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine against COVID-19 caused by Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Inflammopharmacology. 2022 Feb;30(1):149-157. doi: 10.1007/s10787-021-00915-7. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Inflammopharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35099680 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of the Booster of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine among Japanese Adolescents: A Cohort Study.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Nov 12;10(11):1914. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10111914. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36423011 Free PMC article.
-
Timing of BNT162b2 vaccine prior to COVID-19 infection, influence disease severity in patients with hematologic malignancies: Results from a cohort study.Cancer Med. 2023 Nov;12(21):20503-20510. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6397. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37877352 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Vaccine Effectiveness of Booster Doses Against Delta and Omicron Variants Over Follow-up Times Using Longitudinal Meta-analysis.J Res Health Sci. 2024 Sep 30;24(4):e00626. doi: 10.34172/jrhs.2024.161. Epub 2024 Sep 30. J Res Health Sci. 2024. PMID: 39431651 Free PMC article.
-
Association between self-administrated prophylactics and SARS-CoV-2 infection among traditional market vendors from the Central Highlands of Peru: A nested case-control study.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 11;20(7):e0327746. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327746. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40644504 Free PMC article.
-
Humoral and cell-mediated immune responses in HIV-vertically infected young patients after three doses of the BNT162b2 mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 4;14:1301766. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1301766. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38250079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19 Dashboard). https://covid19.who.int/ (2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

