Truncated FGFR2 is a clinically actionable oncogene in multiple cancers
- PMID: 35948633
- PMCID: PMC9436779
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-022-05066-5
Truncated FGFR2 is a clinically actionable oncogene in multiple cancers
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Truncated FGFR2 is a clinically actionable oncogene in multiple cancers.Nature. 2022 Sep;609(7929):E13. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05287-8. Nature. 2022. PMID: 36050473 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
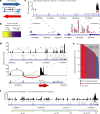
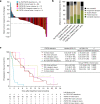
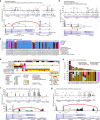
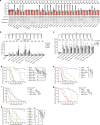
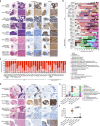
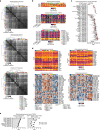
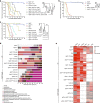
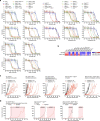
Somatic hotspot mutations and structural amplifications and fusions that affect fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (encoded by FGFR2) occur in multiple types of cancer1. However, clinical responses to FGFR inhibitors have remained variable1-9, emphasizing the need to better understand which FGFR2 alterations are oncogenic and therapeutically targetable. Here we apply transposon-based screening10,11 and tumour modelling in mice12,13, and find that the truncation of exon 18 (E18) of Fgfr2 is a potent driver mutation. Human oncogenomic datasets revealed a diverse set of FGFR2 alterations, including rearrangements, E1-E17 partial amplifications, and E18 nonsense and frameshift mutations, each causing the transcription of E18-truncated FGFR2 (FGFR2ΔE18). Functional in vitro and in vivo examination of a compendium of FGFR2ΔE18 and full-length variants pinpointed FGFR2-E18 truncation as single-driver alteration in cancer. By contrast, the oncogenic competence of FGFR2 full-length amplifications depended on a distinct landscape of cooperating driver genes. This suggests that genomic alterations that generate stable FGFR2ΔE18 variants are actionable therapeutic targets, which we confirmed in preclinical mouse and human tumour models, and in a clinical trial. We propose that cancers containing any FGFR2 variant with a truncated E18 should be considered for FGFR-targeted therapies.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
J.K.L. and R.M are employees of Foundation Medicine and have equity in Roche. I.M.S., H.Z., L.F. and T.C.B. are employees of and have equity in Incyte. G.K.A.-A. has performed research for ActaBiologica, Agios, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Beigene, Berry Genomics, BMS, Casi, Celgene, Exelixis, Genentech/Roche, Halozyme, Incyte, Mabvax, Puma, QED, Sillajen and Yiviva, and has consulted for Agios, Astra Zeneca, Autem, Bayer, Beigene, Berry Genomics, Celgene, CytomX, Debio, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Exelixis, Flatiron, Genentech/Roche, Gilead, Helio, Incyte, Ipsen, Loxo, Merck, MINA, Polaris, QED, Redhill, Silenseed, Sillajen, Sobi, Therabionics, Twoxar, Vector and Yiviva. J.S.R. is an employee of Foundation Medicine, has equity in Roche and is a board member of Celsius Therapeutics. A.V.C. is an employee of Debiopharm International. S.M.A. is an employee of and has equity in EQRX, is a former employee of Foundation Medicine, is a scientific advisory board member of iN Therapeutics and has consulted for Takeda. S.G. has received research funding from M2Gen, has equity in Inspirata and Silagene, and has consulted for Foghorn Therapeutics, Foundation Medicine, Inspirata, Merck, Novartis, Roche and Silagene; his spouse is an employee of and has equity in Merck. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures











References
-
- Katoh M. Fibroblast growth factor receptors as treatment targets in clinical oncology. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019;16:105–122. - PubMed
-
- Van Cutsem E, et al. A randomized, open-label study of the efficacy and safety of AZD4547 monotherapy versus paclitaxel for the treatment of advanced gastric adenocarcinoma with FGFR2 polysomy or gene amplification. Ann. Oncol. 2017;28:1316–1324. - PubMed
-
- Tabernero J, et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of JNJ-42756493, an oral pan–fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015;33:3401–3408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

