Dual-source computed tomography protocols for the pediatric chest - scan optimization techniques
- PMID: 35948645
- PMCID: PMC9365683
- DOI: 10.1007/s00247-022-05468-7
Dual-source computed tomography protocols for the pediatric chest - scan optimization techniques
Abstract
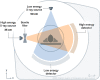
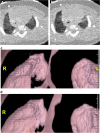
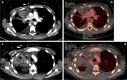
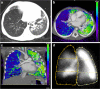
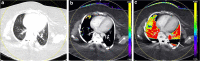
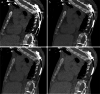
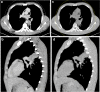
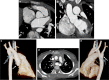
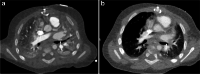
The gold standard for pediatric chest imaging remains the CT scan. An ideal pediatric chest CT has the lowest radiation dose with the least motion degradation possible in a diagnostic scan. Because of the known inherent risks and costs of anesthesia, non-sedate options are preferred. Dual-source CTs are currently the fastest, lowest-dose CT scanners available, utilizing an ultra-high-pitch mode resulting in sub-second CTs. The dual-energy technique, available on dual-source CT scanners, gathers additional information such as pulmonary blood volume and includes relative contrast enhancement and metallic artifact reduction, features that are not available in high-pitch flash mode. In this article we discuss the benefits and tradeoffs of dual-source CT scan modes and tips on image optimization.
Keywords: Chest; Children; Computed tomography; Dual energy; Dual source; Metal reduction; Ultra-high pitch.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Rapp JB, Biko DM, White AM et al (2022) Spectral imaging of the pediatric chest: past, present, and future. Pediatr Radiol. 10.1007/s00247-022-05404-9 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

