Epidemiology and clinical evolution of non-multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) dermatological lesions in pediatric patients affected by SARS-CoV-2 infection: A systematic review of the literature
- PMID: 35948654
- PMCID: PMC9365226
- DOI: 10.1007/s00431-022-04585-7
Epidemiology and clinical evolution of non-multisystem inflammatory syndrome (MIS-C) dermatological lesions in pediatric patients affected by SARS-CoV-2 infection: A systematic review of the literature
Abstract
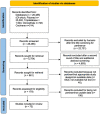
COVID-19 can present with a range of skin manifestations, some of which specific of the pediatric age. The aim of this systematic literature review was to determine the type, prevalence, time of onset, and evolution of cutaneous manifestations associated with COVID-19 in newborns, children, and adolescents, after excluding multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). PubMed, Tripdatabase, ClinicalTrials, and Cochrane Library databases were searched using an ad hoc string for case reports/series and observational studies, published between December 2019 and February 2022. Study quality was assessed using the STROBE and CARE tools. Seventy-three (49 case reports/series and 24 studies) out of 26,545 identified articles were included in the analysis. Dermatological lesions were highly heterogeneous for clinical presentation, time of onset, and association with other COVID-19 manifestations. Overall, they mainly affected the acral portions, and typically presented a favorable outcome. Pseudo-chilblains were the most common.
Conclusions: Mucocutaneous manifestations could be the only/predominant and early manifestation of COVID-19 that could precede other more severe manifestations by days or weeks. Therefore, physicians of all disciplines should be familiar with them.
What is known: • A variety of cutaneous manifestations have been reported in association with COVID-19. • Urticaria, maculopapular, or vesicular rashes can occur at any age, while chilblains and erythema multiforme are more common in children and young patients.
What is new: • Skin lesions related to SARS-CoV-2 infection often show a peculiar acral distribution. • Mucocutaneous lesions of various type may be the only/predominant manifestation of COVID-19; they could present in paucisymptomatic and severely ill patients and occur at different stages of the disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cutaneous acral lesions; Erythema multiforme; Pediatric dermatology; Pseudo-chilblains.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Abrams JY, Oster ME, Godfred-Cato SE, Bryant B, Datta SD, Campbell AP et al (2021) Factors linked to severe outcomes in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) in the USA: A retrospective surveillance study. Lancet Child Adolesc Heal [Internet] 5(5):323–31. Available from: 10.1016/S2352-4642(21)00050-X - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous