Behavioural and functional evidence revealing the role of RBFOX1 variation in multiple psychiatric disorders and traits
- PMID: 35948661
- PMCID: PMC9734045
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-022-01722-4
Behavioural and functional evidence revealing the role of RBFOX1 variation in multiple psychiatric disorders and traits
Abstract
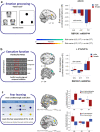
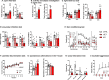
Common variation in the gene encoding the neuron-specific RNA splicing factor RNA Binding Fox-1 Homolog 1 (RBFOX1) has been identified as a risk factor for several psychiatric conditions, and rare genetic variants have been found causal for autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Here, we explored the genetic landscape of RBFOX1 more deeply, integrating evidence from existing and new human studies as well as studies in Rbfox1 knockout mice. Mining existing data from large-scale studies of human common genetic variants, we confirmed gene-based and genome-wide association of RBFOX1 with risk tolerance, major depressive disorder and schizophrenia. Data on six mental disorders revealed copy number losses and gains to be more frequent in ASD cases than in controls. Consistently, RBFOX1 expression appeared decreased in post-mortem frontal and temporal cortices of individuals with ASD and prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia. Brain-functional MRI studies demonstrated that carriers of a common RBFOX1 variant, rs6500744, displayed increased neural reactivity to emotional stimuli, reduced prefrontal processing during cognitive control, and enhanced fear expression after fear conditioning, going along with increased avoidance behaviour. Investigating Rbfox1 neuron-specific knockout mice allowed us to further specify the role of this gene in behaviour. The model was characterised by pronounced hyperactivity, stereotyped behaviour, impairments in fear acquisition and extinction, reduced social interest, and lack of aggression; it provides excellent construct and face validity as an animal model of ASD. In conclusion, convergent translational evidence shows that common variants in RBFOX1 are associated with a broad spectrum of psychiatric traits and disorders, while rare genetic variation seems to expose to early-onset neurodevelopmental psychiatric disorders with and without developmental delay like ASD, in particular. Studying the pleiotropic nature of RBFOX1 can profoundly enhance our understanding of mental disorder vulnerability.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
BF has received educational speaking fees from Medice. AR has served on advisory boards and/or received speaker’s honoraria from Medice, Shire/Takeda, Janssen, SAGE/Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Cyclerion. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

