Effect of preemptive photobiomodulation associated with nimesulide on the postsurgical outcomes, oxidative stress, and quality of life after third molar surgery: a randomized, split-mouth, controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 35948699
- PMCID: PMC9365445
- DOI: 10.1007/s00784-022-04649-w
Effect of preemptive photobiomodulation associated with nimesulide on the postsurgical outcomes, oxidative stress, and quality of life after third molar surgery: a randomized, split-mouth, controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study is to compare the effect of photobiomodulation with low-level laser therapy (LLLT) and nimesulide on inflammatory parameters, biomarkers of oxidative stress and inflammation, and quality of life after lower third molar (L3M) surgery.
Material and methods: A randomized, two-factor, triple-blind, controlled, split-mouth clinical trial was performed with 40 volunteers who required bilateral L3M removal. Patients were allocated depending on the use or not of 100 mg nimesulide 1 hbefore surgery, as well as the use or not of LLLT in the preoperative period.
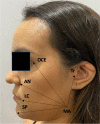
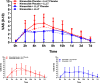
Results: Pain peaks occurred after 6 h (nimesulide-placebo [N-P] group) and 8 h (nimesulide group). In the N-P group, LLLT resulted in significantly lower mean pain scores than the subgroup without LLLT after 4 h (p = 0.009) and 6 h (p = 0.048). As for edema, a shorter distance between the mandibular angle and the outer canthus of the eyes after 7 days (p = 0.037) and a smaller cumulative effect (p = 0.036) were observed in the N-P group associated with LLLT. A direct effect between LLLT (p = 0.047) and a reduction in the mean scores of overall dissatisfaction with quality of life was detected.
Conclusions: Preemptive use of nimesulide only delayed peak pain. LLLT reduced edema, trismus, and contributed to a better perception of quality of life. Nimesulide inhibits peroxidation by increasing GSH and stopping neutrophil migration. The benefit of the association of both strategies was not superior to the use of LLLT alone.
Clinical relevance: Translational study with impact on clinical-surgical protocols involving L3M surgery related to pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods.
Keywords: Analgesia; Anti-inflammatory agents, Non-steroidal; Low-level light therapy; Oxidative stress; Quality of life; Third molar.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
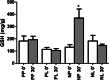
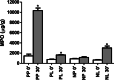
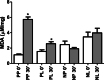
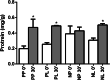
References
-
- Costa FWG, Soares ECS, Esses DFS, Silva PGB, Bezerra TP, Scarparo HC, Ribeiro TR, Fonteles CSR. A split-mouth, randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled study to analyze the pre-emptive effect of etoricoxib 120 mg on inflammatory events following removal of unerupted mandibular third molars. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;44:1166–1174. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2015.06.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Albuquerque AFM, Fonteles CSR, Do Val DR, Chaves HV, Bezerra MM, Pereira KMA, Silva PGB, De Lima BB, Soares ECS, Ribeiro TR, Costa FWG. Effect of pre-emptive analgesia on clinical parameters and tissue levels of TNF-a and IL-1b in third molar surgery: a triple-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;46:1615–1625. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2017.05.007. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

