Tax1 banding protein 1 exacerbates heart failure in mice by activating ITCH-P73-BNIP3-mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis
- PMID: 35948751
- PMCID: PMC9525615
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-022-00950-2
Tax1 banding protein 1 exacerbates heart failure in mice by activating ITCH-P73-BNIP3-mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis
Abstract
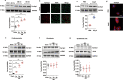
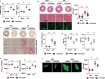
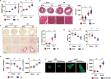
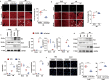
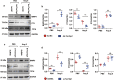
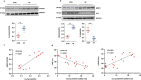
Tax1 banding protein 1 (Tax1bp1) was originally identified as an NF-κB regulatory protein that participated in inflammatory, antiviral and innate immune processes. Tax1bp1 also functions as an autophagy receptor that plays a role in autophagy. Our previous study shows that Tax1bp1 protects against cardiomyopathy in STZ-induced diabetic mice. In this study we investigated the role of Tax1bp1 in heart failure. Pressure overload-induced heart failure model was established in mice by aortic banding (AB) surgery, and angiotensin II (Ang II)-induced heart failure model was established by infusion of Ang II through osmotic minipump for 4 weeks. We showed that the expression levels of Tax1bp1 in the heart were markedly increased 2 and 4 weeks after AB surgery. Knockdown of Tax1bp1 in mouse hearts significantly ameliorated both AB- and Ang II infusion-induced heart failure parameters. On the contrary, AB-induced heart failure was aggravated in cardiac-specific Tax1bp1 transgenic mice. Similar results were observed in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (NRCMs) under Ang II insult. We demonstrated that the pro-heart failure effect of Tax1bp1 resulted from its interaction with the E3 ligase ITCH to promote the transcription factor P73 ubiquitination and degradation, causing enhanced BCL2 interacting protein 3 (BNIP3)-mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Knockdown ITCH or BNIP3 in NRCMs significantly reduced Ang II-induced apoptosis in vitro. Similarly, BNIP3 knockdown attenuated heart failure in cardiac-specific Tax1bp1 transgenic mice. In the left ventricles of heart failure patients, Tax1bp1 expression level was significantly increased; Tax1bp1 gene expression was negatively correlated with left ventricular ejection fraction in heart failure patients. Collectively, the Tax1bp1 increase in heart failure enhances ITCH-P73-BNIP3-mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis and induced cardiac injury. Tax1bp1 may serve as a potent therapeutic target for the treatment of heart failure.• Cardiac Tax1bp1 transgene mice were more vulnerable to cardiac dysfunction under stress.• Cardiac Tax1bp1 transgene mice were more vulnerable to cardiac dysfunction under stress.• Knockout of Tax1bp1 in mouse hearts ameliorated heart failure induced by pressure overload.• Tax1bp1 interacts with the E3 ligase Itch to promote P73 ubiquitination and degradation, causing enhanced BNIP3-mediated apoptosis.• Tax1bp1 may become a target of new therapeutic methods for treating heart failure.
Keywords: BCL2 interacting protein 3; ITCH; P73; Tax1 banding protein 1; apoptosis; heart failure.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

