How to discern external acoustic waves in a piezoelectric neuron under noise?
- PMID: 35948818
- PMCID: PMC9411441
- DOI: 10.1007/s10867-022-09611-1
How to discern external acoustic waves in a piezoelectric neuron under noise?
Abstract
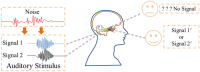
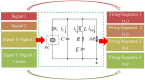
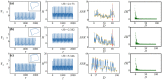
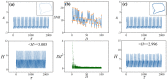
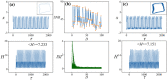
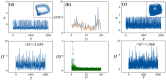
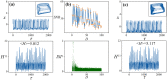
Biological neurons keep sensitive to external stimuli and appropriate firing modes can be triggered to give effective response to external chemical and physical signals. A piezoelectric neural circuit can perceive external voice and nonlinear vibration by generating equivalent piezoelectric voltage, which can generate an equivalent trans-membrane current for inducing a variety of firing modes in the neural activities. Biological neurons can receive external stimuli from more ion channels and synapse synchronously, but the further encoding and priority in mode selection are competitive. In particular, noisy disturbance and electromagnetic radiation make it more difficult in signals identification and mode selection in the firing patterns of neurons driven by multi-channel signals. In this paper, two different periodic signals accompanied by noise are used to excite the piezoelectric neural circuit, and the signal processing in the piezoelectric neuron driven by acoustic waves under noise is reproduced and explained. The physical energy of the piezoelectric neural circuit and Hamilton energy in the neuron driven by mixed signals are calculated to explain the biophysical mechanism of auditory neuron when external stimuli are applied. It is found that the neuron prefers to respond to the external stimulus with higher physical energy and the signal which can increase the Hamilton energy of the neuron. For example, stronger inputs used to inject higher energy and it is detected and responded more sensitively. The involvement of noise is helpful to detect the external signal under stochastic resonance, and the additive noise changes the excitability of neuron as the external stimulus. The results indicate that energy controls the firing patterns and mode selection in neurons, and it provides clues to control the neural activities by injecting appropriate energy into the neurons and network.
Keywords: Firing patterns; Hamilton energy; Noise; Piezoelectric neuron; Stochastic resonance.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A memristive neuron and its adaptability to external electric field.Chaos. 2023 Feb;33(2):023110. doi: 10.1063/5.0136195. Chaos. 2023. PMID: 36859211
-
Energy controls wave propagation in a neural network with spatial stimuli.Neural Netw. 2024 Mar;171:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2023.11.042. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Neural Netw. 2024. PMID: 38091753
-
A neuron model with nonlinear membranes.Cogn Neurodyn. 2024 Apr;18(2):673-684. doi: 10.1007/s11571-023-10017-5. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Cogn Neurodyn. 2024. PMID: 38699608 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability and energy function of an oscillator and map neuron.Biosystems. 2025 May;251:105443. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2025.105443. Epub 2025 Mar 3. Biosystems. 2025. PMID: 40044073
-
Electrical Signaling Beyond Neurons.Neural Comput. 2024 Sep 17;36(10):1939-2029. doi: 10.1162/neco_a_01696. Neural Comput. 2024. PMID: 39141803 Review.
Cited by
-
Energy-guided synapse coupling between neurons under noise.J Biol Phys. 2023 Mar;49(1):49-76. doi: 10.1007/s10867-022-09622-y. Epub 2023 Jan 14. J Biol Phys. 2023. PMID: 36640246 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of internal and external chaotic stimuli on synchronization of piezoelectric auditory neurons in coupled time-delay systems.Cogn Neurodyn. 2024 Aug;18(4):2111-2126. doi: 10.1007/s11571-023-10042-4. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Cogn Neurodyn. 2024. PMID: 39104671 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

