The feasibility, safety and short-term clinical efficacy of laparoscopic anterior resection of rectal cancer with left colonic artery (LCA) preservation and natural orifice specimen extraction (NOSE)
- PMID: 35948902
- PMCID: PMC9364571
- DOI: 10.1186/s12893-022-01719-4
The feasibility, safety and short-term clinical efficacy of laparoscopic anterior resection of rectal cancer with left colonic artery (LCA) preservation and natural orifice specimen extraction (NOSE)
Abstract
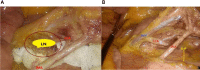
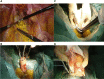
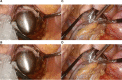
Background: Natural orifice specimen extraction surgery (NOSES) has the advantages of less postoperative pain, fast bowel function recovery, reduced hospital stay and better cosmetic effects. In our centre, anterior resection of rectal cancer with preservation of the left colonic artery (LCA) was performed using NOSES. The feasibility, safety and short-term clinical efficacy of the technique were discussed.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed on 19 patients who underwent laparoscopic anterior resection of rectal cancer with left colonic artery preservation and natural orifice specimen extraction in the Gastrointestinal Surgery Center of Sichuan Cancer Hospital from September 2018 to December 2019. General information about the patients, perioperative data and short-term postoperative results were analysed.
Results: All operations were completed smoothly, with an average operation duration of 304.36 ± 45.04 min, intraoperative bleeding of 76.31 ± 61.12 ml, first time off bed of 14.42 ± 3.56 h, first time to anus exhaust of 15.26 ± 8.92 h, first time to liquid diet of 2.94 ± 1.12 days, and average postoperative stay of 10.21 ± 3.13 days. Two patients developed temporary intestinal obstruction, and one patient developed pulmonary infection. All of them recovered well after active supportive treatment and were successfully discharged.
Conclusion: Laparoscopic NOSES for rectal cancer with left colon artery preservation is safe and feasible, with satisfactory short-term results, and is worthy of further clinical investigation.
Keywords: Laparoscopic surgery; Left colon artery; Natural orifice specimen extraction (NOSE); Rectal cancer.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Tsuchiya S. Surgery for rectal cancer. Auton Nervous Syst. 1983;37:1367.
-
- Clinical Outcomes of Surgical Therapy Study Group. Nelson H, Sargent DJ, Wieand HS, Fleshman J, Anvari M, Stryker SJ, Beart RW, Hellinger M, Flanagan R, Peters W, Ota D. A comparison of laparoscopically assisted and open colectomy for colon cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(20):2050–2059. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa032651. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Colon Cancer Laparoscopic or Open Resection Study Group. Buunen M, Veldkamp R, Hop WC, Kuhry E, Jeekel J, Haglind E, Påhlman L, Cuesta MA, Msika S, Morino M, Lacy A, Bonjer HJ. Survival after laparoscopic surgery versus open surgery for colon cancer: long-term outcome of a randomised clinical trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(1):44–52. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70310-3. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

