Harpagoside attenuates local bone Erosion and systemic osteoporosis in collagen-induced arthritis in mice
- PMID: 35948905
- PMCID: PMC9364518
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-022-03694-y
Harpagoside attenuates local bone Erosion and systemic osteoporosis in collagen-induced arthritis in mice
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease that causes local bone erosion and systemic osteoporosis. Harpagoside (HAR), an iridoid glycoside, has various pharmacological effects on pain, arthritis, and inflammation. Our previous study suggests that HAR is more deeply involved in the mechanism of bone loss caused by inflammatory stimuli than hormonal changes. Here, we identified the local and systemic bone loss inhibitory effects of HAR on RA and its intracellular mechanisms using a type 2 collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mouse model.
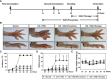
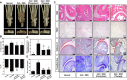
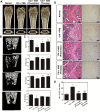
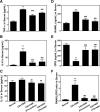
Methods: The anti-osteoporosis and anti-arthritic effects of HAR were evaluated on bone marrow macrophage in vitro and CIA in mice in vivo by obtaining clinical scores, measuring hind paw thickness and inflammatory cytokine levels, micro-CT and histopathological assessments, and cell-based assay.
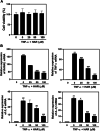
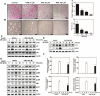
Results: HAR markedly reduced the clinical score and incidence rate of CIA in both the prevention and therapy groups. Histological analysis demonstrated that HAR locally ameliorated the destruction of bone and cartilage and the formation of pannus. In this process, HAR decreased the expression of inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1β in the serum of CIA mice. Additionally, HAR downregulated the expression of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand and upregulated that of osteoprotegerin. HAR suppressed systemic bone loss by inhibiting osteoclast differentiation and osteoclast marker gene expression in a CIA mouse model.
Conclusions: Taken together, these findings show the beneficial effect of HAR on local symptoms and systemic bone erosion triggered by inflammatory arthritis.
Keywords: Collagen-induced arthritis model; Harpagoside; Inflammation; Osteoclasts; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that this article involves no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protection against cartilage and bone destruction by systemic interleukin-4 treatment in established murine type II collagen-induced arthritis.Arthritis Res. 1999;1(1):81-91. doi: 10.1186/ar14. Epub 1999 Oct 26. Arthritis Res. 1999. PMID: 11056663 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-arthritic and anti-inflammatory effects of (-)-Epicatechin-3-O-β-d-allopyranoside, a constituent of Davallia formosana.Phytomedicine. 2019 Jan;52:12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.192. Epub 2018 Sep 18. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30599891
-
Melittin acupoint injection in attenuating bone erosion in collagen-induced arthritis mice via inhibition of the RANKL/NF-κB signaling pathway.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Sep 1;13(9):5996-6013. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-254. Epub 2023 Jul 20. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 37711782 Free PMC article.
-
RANK, RANKL and osteoprotegerin in arthritic bone loss.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2005 Feb;38(2):161-70. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2005000200004. Epub 2005 Feb 15. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2005. PMID: 15785827 Review.
-
Animal Models of Bone Loss in Inflammatory Arthritis: from Cytokines in the Bench to Novel Treatments for Bone Loss in the Bedside-a Comprehensive Review.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016 Aug;51(1):27-47. doi: 10.1007/s12016-015-8522-7. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26634933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Saururus chinensis (Lour.) Baill. extract promotes skeletal muscle cell differentiation by positively regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and AKT/mTOR signaling in vitro.Mol Med Rep. 2024 Jul;30(1):125. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13250. Epub 2024 May 24. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38785149 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

