The role of dental pain and psychosocial factors on the relationship between dental caries and oral health-related quality of life in children
- PMID: 35948932
- PMCID: PMC9364536
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-022-02372-2
The role of dental pain and psychosocial factors on the relationship between dental caries and oral health-related quality of life in children
Erratum in
-
Correction: The role of dental pain and psychosocial factors on the relationship between dental caries and oral health-related quality of life in children.BMC Oral Health. 2022 Nov 4;22(1):467. doi: 10.1186/s12903-022-02541-3. BMC Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 36333685 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
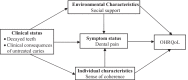
Background: To examine the role of dental pain, sense of coherence (SOC) and social support on the relationship between dental caries and oral health-related quality of life (OHRQoL) in children aged 12 years.
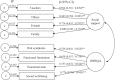
Methods: A cross-sectional study involving 400 schoolchildren selected from public schools in a socioeconomically disadvantaged region in the city of Manaus, Brazil was carried out. The predictors of OHRQoL were selected according to the Wilson and Cleary theoretical model, including number of decayed teeth and its clinical consequence (component D of the DMFT index and PUFA/pufa index), dental pain (symptom status), and SOC and social support (individual and environmental characteristics). Statistical analysis was conducted through structural equation modelling and multivariable negative binomial regression. The significance level established for all analyses was 5%.
Results: Number of dental caries was indirectly linked with OHRQoL (β = 0.19, 95% CI 0.11/0.29) through dental pain, SOC and social support. Clinical consequences of untreated caries directly predicted poor OHRQoL (β = 0.12, 95% CI 0.01/0.23). Dental pain, SOC and social support did not moderate the effect of dental caries measures on OHRQoL.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest the role of dental pain, SOC and social support as mediator factors on the link between dental caries and OHRQoL. Tackling dental caries along with psychosocial factors may attenuated the impact of oral health on OHRQoL in children.
Keywords: Dental caries; Dental pain; Quality of life; Sense of coherence; Social support.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

