Spatial distribution and associated factors of community based health insurance coverage in Ethiopia: further analysis of Ethiopian demography and health survey, 2019
- PMID: 35948950
- PMCID: PMC9364505
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-022-13950-y
Spatial distribution and associated factors of community based health insurance coverage in Ethiopia: further analysis of Ethiopian demography and health survey, 2019
Abstract
Background: Community-Based Health Insurance is an emerging concept for providing financial protection against the cost of illness and improving access to quality health services for low-income households excluded from formal insurance and taken as a soft option by many countries. Therefore, exploring the spatial distribution of health insurance is crucial to prioritizing and designing targeted intervention policies in the country.
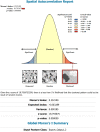
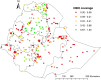
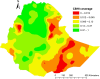
Methods: A total of 8,663 households aged 15-95 years old were included in this study. The Bernoulli model was used by applying Kulldorff methods using the SaTScan software to analyze the purely spatial clusters of community based health insurance. ArcGIS version 10.3 was used to visualize the distribution of community-based health insurance coverage across the country. Mixed-effect logistic regression analysis was also used to identify predictors of community-based health insurance coverage.
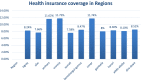
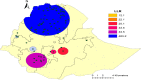
Results: Community based health insurance coverage among households had spatial variations across the country by regions (Moran's I: 0.252, p < 0.0001). Community based health insurance in Amhara (p < 0.0001) and Tigray (p < 0.0001) regions clustered spatially. Age from 15-29 and 30-39 years (Adjusted Odds Ratio 0.46(AOR = 0.46, CI: 0.36,0.60) and 0.77(AOR = 0.77, CI: 0.63,0.96), primary education level 1.57(AOR = 1.57, CI: 1.15,2.15), wealth index of middle and richer (1.71(AOR = 1.71, CI: 1.30,2.24) and 1.79(AOR = 1.79, CI: 1.34,2.41), family size > 5, 0.82(AOR = 0.82, CI: 0.69,0.96),respectively and regions Afar, Oromia, Somali, Benishangul Gumuz, SNNPR, Gambella, Harari, Addis Ababa and Dire Dawa was 0.002(AOR = 0.002, CI: 0.006,0.04), 0.11(AOR = 0.11, CI: 0.06,0.21) 0.02(AOR = 0.02, CI: 0.007,0.04), 0.04(AOR = 0.04, CI: 0.02,0.08), 0.09(AOR = 0.09, CI: 0.05,0.18),0.004(AOR = 0.004,CI:0.02,0.08),0.06(AOR = 0.06,CI:0.03,0.14), 0.07(AOR = 0.07, CI: 0.03,0.16) and 0.03(AOR = 0.03, CI: 0.02,0.07) times less likely utilize community based health insurance than the Amhara region respectively in Ethiopia.
Conclusion: Community based health insurance coverage among households in Ethiopia was found very low still. The government needs to develop consistent financial and technical support and create awareness for regions with lower health insurance coverage.
Keywords: Community based health insurance coverage; EDHS 2019; Ethiopia; Spatial distribution; Universal health coverage.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kebede SA, Liyew AM, Tesema GA, Agegnehu CD, Teshale AB, Alem AZ, et al. Spatial distribution and associated factors of health insurance coverage in Ethiopia: further analysis of Ethiopia demographic and health survey, 2016. Arch Public Health. 2020;78(1):1–10. doi: 10.1186/s13690-020-00407-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Demographic E. Health Survey 2011 Addis Ababa, Ethiopia and Calverton, Maryland, USA: Central Statistical Agency and ICF International. Ababa, Ethiopia: Central Statistical Agency; 2012.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

