Serum interleukin-38 levels correlated with insulin resistance, liver injury and lipids in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 35948957
- PMCID: PMC9364532
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-022-01676-0
Serum interleukin-38 levels correlated with insulin resistance, liver injury and lipids in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
Background: Insulin resistance, liver injury and dyslipidemia are reported in non-alcoholic fat liver disease (NAFLD) patients. Interleukin (IL)-38 may take part in the pathophysiology of insulin resistance. Nevertheless, the function of IL-38 in NAFLD is unknown. Herein, we determined whether serum IL-38 level might be utilised as a biochemical marker for diagnosing NAFLD.
Methods: NAFLD patients and healthy participants (n = 91 each) were enrolled. Circulating serum IL-38 levels were detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Other metabolic and inflammatory indices related to NAFLD were also assessed.
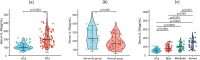
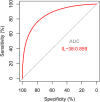
Results: Patients with NAFLD had higher serum IL-38 levels than healthy individuals. Significantly higher serum IL-38 levels were found in patients with severe and moderate NAFLD than in patients with mild NAFLD. IL-38 showed a significant correlation with parameters of insulin resistance, inflammation, and liver enzyme in NAFLD cases. Anthropometric, insulin resistance, inflammatory parameters, lipids and frequency of NAFLD showed significant differences among the serum IL-38 level tertiles. Participants in the 2nd and 3rd tertiles of serum IL-38 levels had a greater risk of NAFLD than those in the 1st tertile. Furthermore, IL-38 ROC curve showed a high area under ROC with 0.861.
Conclusions: It is possible for serum IL-38 to be a biomarker for NAFLD.
Keywords: Biomarker; IL-38; Inflammation; Insulin resistance; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no conflict of interest existed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CCN3/NOV Serum Levels in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Patients in Comparison with the Healthy Group and its Correlation with TNF-α and IL-6.Curr Mol Med. 2025;25(5):605-613. doi: 10.2174/0115665240285539240214111947. Curr Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 38415473
-
Interleukin Levels and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis: An Analytical Case Control Study.Indian J Dermatol. 2023 Jul-Aug;68(4):377-384. doi: 10.4103/ijd.ijd_1015_22. Indian J Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37822394 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose homeostasis, insulin resistance and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Beneficial effects of supplementation with microalgae Chlorella vulgaris: A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial.Clin Nutr. 2017 Aug;36(4):1001-1006. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2016.07.004. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Clin Nutr. 2017. PMID: 27475283 Clinical Trial.
-
Metabolic syndrome and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Is insulin resistance the link?Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Dec 15;418 Pt 1:55-65. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.02.018. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25724480 Review.
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and dyslipidemia: An update.Metabolism. 2016 Aug;65(8):1109-23. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2016.05.003. Epub 2016 May 13. Metabolism. 2016. PMID: 27237577 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-38 and Insulin Resistance.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(6):611-616. doi: 10.2174/1871530323666230911114150. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 37702180
-
Metabolic regulation of the immune system in health and diseases: mechanisms and interventions.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Oct 9;9(1):268. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01954-6. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39379377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbiota in insulin resistance: a bibliometric analysis.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2024 Feb 14;23(1):173-188. doi: 10.1007/s40200-023-01342-x. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2024. PMID: 38932838 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

