Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic parameters of vancomycin for predicting clinical outcome of enterococcal bacteremia
- PMID: 35948963
- PMCID: PMC9364583
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-022-07668-w
Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic parameters of vancomycin for predicting clinical outcome of enterococcal bacteremia
Abstract
Purpose: To find pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic parameters of vancomycin associated with the optimal outcome of severe infection due to Enterococcus species.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed enterococcal bacteremia cases treated with vancomycin from January 2015 to December 2020. The primary outcome was 30-day mortality. We calculated cutoff values of the ratio of vancomycin area under the concentration-time curve over 24 h to the minimum inhibitory concentration (AUC24/MIC) and trough concentration (Ctrough) during the initial 72 h of treatment. The optimal cutoff value was determined using the Youden index. Binary variables created based on these cutoffs were further assessed using multivariable analysis.
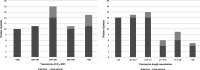
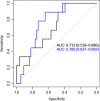
Results: A total of 65 patients were included. The majority (87.7%) had solid or hematologic malignancies. Thirty-day mortality and nephrotoxicity occurred in nine (13.4%) and 14 (21.5%) patients, respectively. Both vancomycin AUC24/MIC and Ctrough showed fair performance in predicting 30-day mortality (AUC of receiver-operator curve for AUC24/MIC, 0.712; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.539-0.886; AUC for Ctrough, 0.760; 95% CI 0.627-0.892; pairwise AUC comparison: p = 0.570). Ctrough ≥ 13.94 μg/mL, but not AUC24/MIC ≥ 504, had a significant association with 30-day mortality after adjusting for confounders (odds ratio, 8.40; 95% CI 1.60-86.62; p = 0.010).
Conclusion: Mean Ctrough ≥ 13.94 μg/mL during the initial 72 h was associated with higher 30-day mortality in enterococcal bacteremia. Further studies are warranted to elucidate optimal pharmacokinetic targets for enterococcal bacteremia.
Keywords: AUC/MIC; Enterococcus; PK/PD; Trough; Vancomycin.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Rybak MJ, Le J, Lodise TP, Levine DP, Bradley JS, Liu C, et al. Therapeutic monitoring of vancomycin for serious methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: a revised consensus guideline and review by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2020;77(11):835–864. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/zxaa036. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

