Dapagliflozin Improves Cardiac Autonomic Function Measures in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy
- PMID: 35949125
- PMCID: PMC9682606
- DOI: 10.5152/AnatolJCardiol.2022.1934
Dapagliflozin Improves Cardiac Autonomic Function Measures in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy
Abstract
Background: Cardiac autonomic neuropathy is a frequent complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy, in which sympathetic tone predominates over parasympathetic activity, increases both cardiovascular morbidity and mortality and unfortunately has no definitive treatment. Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors have been suggested to reduce sympathetic nervous system activity, based on the results from previous studies. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect of 24-week treatment with dapagliflozin, a sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor, on cardiac autonomic function measures in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiac autonomic neuropathy.
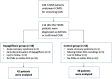
Methods: Dapagliflozin 10 mg/day (n=42) or non-sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor oral antidiabetic(s) (n=38) was added to the treatment of patients whose glycemic control could not be achieved with existing treatments. The patients with definite or confirmed cardiac autonomic neuropathy diagnosed by cardiovascular autonomic reflex tests underwent 24-hour Holter-electrocardiogram recordings to obtain heart rate variability and heart rate turbulence parameters before starting additional medication and after a 24-week treatment period.
Results: In-group analyses showed that dapagliflozin 10 mg/day for 24 weeks improved heart rate variability and heart rate turbulence parameters and decreased the frequency of ventricular premature beats relative to their baseline values. No such findings were observed in the control group despite similar glycemic control. Comparisons between dapagliflozin group and the control group showed that these effects of dapagliflozin were significantly better than non-sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor oral antidiabetics.
Conclusion: Dapagliflozin improves measures of cardiac autonomic function compared to the control group in type 2 diabetic patients with cardiac autonomic neuropathy. This intergroup benefit, demonstrated for the first time, may be promising for the regression of cardiac autonomic neuropathy with sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors on Sympathetic Nervous System Activity Detected by Sympathetic Activity Index and LF/HF Ratio in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars. 2022 Sep;50(6):415-421. doi: 10.5543/tkda.2022.22403. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars. 2022. PMID: 35976237
-
Dapagliflozin and measures of cardiovascular autonomic function in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D).J Diabetes Complications. 2021 Aug;35(8):107949. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2021.107949. Epub 2021 May 15. J Diabetes Complications. 2021. PMID: 34024686 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Dapagliflozin on Heart Failure and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Circulation. 2019 May 28;139(22):2528-2536. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.040130. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Circulation. 2019. PMID: 30882238 Clinical Trial.
-
Dapagliflozin: a new sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor for treatment of type 2 diabetes.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015 Mar 1;72(5):361-72. doi: 10.2146/ajhp140168. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2015. PMID: 25694411 Review.
-
Dapagliflozin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus - an update.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021 Dec;22(17):2303-2310. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2021.1953471. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34281456 Review.
Cited by
-
SGLT2 Inhibitors as Potential Anticancer Agents.Biomedicines. 2023 Jun 30;11(7):1867. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071867. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remodeling of the Intracardiac Ganglia During the Development of Cardiovascular Autonomic Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutics.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 20;25(22):12464. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212464. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treating heart failure by targeting the vagus nerve.Heart Fail Rev. 2024 Nov;29(6):1201-1215. doi: 10.1007/s10741-024-10430-w. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Heart Fail Rev. 2024. PMID: 39117958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetes-Induced Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy: Impact on Heart Function and Prognosis.Biomedicines. 2022 Dec 15;10(12):3258. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123258. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36552014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Improvements of cardiac function and metabolic parameters by sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors with no significant effects on sympathetic or parasympathetic activity in chronic heart failure.Heart Vessels. 2025 Aug 7. doi: 10.1007/s00380-025-02592-w. Online ahead of print. Heart Vessels. 2025. PMID: 40770087
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

