Soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor improves early risk stratification in cardiogenic shock
- PMID: 35949144
- PMCID: PMC9629697
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjacc/zuac096
Soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor improves early risk stratification in cardiogenic shock
Abstract
Aims: Soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) is a biomarker reflecting the level of immune activation. It has been shown to have prognostic value in acute coronary syndrome and heart failure as well as in critical illness. Considering the complex pathophysiology of cardiogenic shock (CS), we hypothesized suPAR might have prognostic properties in CS as well. The aim of this study was to assess the kinetics and prognostic utility of suPAR in CS.
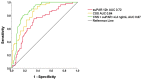
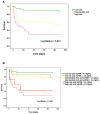
Methods and results: SuPAR levels were determined in serial plasma samples (0-96 h) from 161 CS patients in the prospective, observational, multicentre CardShock study. Kinetics of suPAR, its association with 90-day mortality, and additional value in risk-stratification were investigated. The median suPAR-level at baseline was 4.4 [interquartile range (IQR) 3.2-6.6)] ng/mL. SuPAR levels above median were associated with underlying comorbidities, biomarkers reflecting renal and cardiac dysfunction, and higher 90-day mortality (49% vs. 31%; P = 0.02). Serial measurements showed that survivors had significantly lower suPAR levels at all time points compared with nonsurvivors. For risk stratification, suPAR at 12 h (suPAR12h) with a cut-off of 4.4 ng/mL was strongly associated with mortality independently of established risk factors in CS: OR 5.6 (95% CI 2.0-15.5); P = 0.001) for death by 90 days. Adding suPAR12h > 4.4 ng/mL to the CardShock risk score improved discrimination identifying high-risk patients originally categorized in the intermediate-risk category.
Conclusion: SuPAR associates with mortality and improves risk stratification independently of other previously known risk factors in CS patients.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cardiogenic shock; Risk stratification; suPAR.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: J.P. received honoraria for lectures from Orion Pharma, Roche Diagnostics, Novartis, Astra and Servier. A.M. reports personal fees from Orion, Servier, Otsuka, Philips, Sanofi, Adrenomed, Epygon and Fire 1 and grants and personal fees from 4TEEN4, Abbott, Roche and Sphyngotec. All other authors have no conflicts to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Kohsaka S, Menon V, Lowe AM, Lange M, Dzavik V, Sleeper LA, Hochman JS, SHOCK Investigators . Systemic inflammatory response syndrome after acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock. Arch Intern Med 2005;165:1643–1650. - PubMed
-
- Chavakis T, Willuweit AK, Lupu F, Preissner KT, Kanse SM. Release of soluble urokinase receptor from vascular cells. Thromb Haemost 2001;86:686–693. - PubMed
-
- Donadello K, Scolletta S, Taccone FS, Covajes C, Santonocito C, Cortes DO, Grazulyte D, Gottin L, Vincent J-L. Soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor as a prognostic biomarker in critically ill patients. J Crit Care 2014;29:144–149. - PubMed

