Modular capsid decoration boosts adenovirus vaccine-induced humoral immunity against SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 35949171
- PMCID: PMC9364715
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.08.002
Modular capsid decoration boosts adenovirus vaccine-induced humoral immunity against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
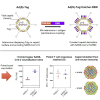
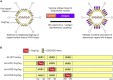
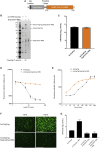
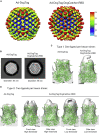
Adenovirus vector vaccines have been widely and successfully deployed in response to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). However, despite inducing potent T cell immunity, improvement of vaccine-specific antibody responses upon homologous boosting is modest compared with other technologies. Here, we describe a system enabling modular decoration of adenovirus capsid surfaces with antigens and demonstrate potent induction of humoral immunity against these displayed antigens. Ligand attachment via a covalent bond was achieved using a protein superglue, DogTag/DogCatcher (similar to SpyTag/SpyCatcher), in a rapid and spontaneous reaction requiring only co-incubation of ligand and vector components. DogTag was inserted into surface-exposed loops in the adenovirus hexon protein to allow attachment of DogCatcher-fused ligands on virus particles. Efficient coverage of the capsid surface was achieved using various ligands, with vector infectivity retained in each case. Capsid decoration shielded particles from vector neutralizing antibodies. In prime-boost regimens, adenovirus vectors decorated with the receptor-binding domain of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike induced >10-fold higher SARS-CoV-2 neutralization titers compared with an undecorated vector encoding spike. Importantly, decorated vectors achieved equivalent or superior T cell immunogenicity against encoded antigens compared with undecorated vectors. We propose capsid decoration using protein superglues as a novel strategy to improve efficacy and boostability of adenovirus-based vaccines and therapeutics.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; adenovirus; protein superglue; vaccine vector; vector engineering.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests M.D.J.D., L.M.R., R.A.R., and L.A.H.B. are employees of SpyBiotech Ltd. S.B. is CSO and co-founder of SpyBiotech Ltd. S.J.D. and M.H. are co-founders of SpyBiotech Ltd, and M.H. is also an author on a number of patents relating to protein superglues, including the DogTag/DogCatcher technology. C.G., J.M.J.-G., K.J.D., and M.H.M. declare no competing interests.
Figures


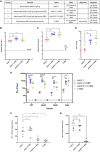
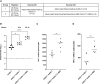
References
-
- Voysey M., Clemens S.A.C., Madhi S.A., Weckx L.Y., Folegatti P.M., Aley P.K., Angus B., Baillie V.L., Barnabas S.L., Bhorat Q.E., Bibi S., et al. Safety and efficacy of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine (AZD1222) against SARS-CoV-2: an interim analysis of four randomised controlled trials in Brazil, South Africa, and the UK. Lancet. 2021;397:99–111. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32661-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sadoff J., Gray G., Vandebosch A., Cárdenas V., Shukarev G., Grinsztejn B., Goepfert P.A., Truyers C., Fennema H., Spiessens B., Offergeld K., et al. Safety and efficacy of single-dose Ad26.COV2.S vaccine against covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021;384:2187–2201. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2101544. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Logunov D.Y., Dolzhikova I.V., Shcheblyakov D.V., Tukhvatulin A.I., Zubkova O.V., Dzharullaeva A.S., Kovyrshina A.V., Lubenets N.L., Grousova D.M., Erokhova A.S., et al. Safety and efficacy of an rAd26 and rAd5 vector-based heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccine: an interim analysis of a randomised controlled phase 3 trial in Russia. Lancet. 2021;397:671–681. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00234-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu F.C., Guan X.H., Li Y.H., Huang J.Y., Jiang T., Hou L.H., Li J.X., Yang B.F., Wang L., Wang W.J., Wu S.P., et al. Immunogenicity and safety of a recombinant adenovirus type-5-vectored COVID-19 vaccine in healthy adults aged 18 years or older: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2020;396:479–488. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31605-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

