Real-Time, Nondestructive Optical Feedback Systems for Infrared Laser Sealing of Blood Vessels
- PMID: 35949201
- PMCID: PMC9361299
- DOI: 10.1117/12.2605600
Real-Time, Nondestructive Optical Feedback Systems for Infrared Laser Sealing of Blood Vessels
Abstract
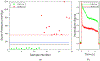
High-power infrared (IR) diode lasers are capable of sealing blood vessels during surgery. This study characterizes an optical feedback system for real-time, nondestructive identification of vessel seals. A low power, red aiming beam (635 nm) was used for diagnostics, co-aligned with a therapeutic high-power IR beam (1470 nm). The IR laser delivered either 30 W for 5 s for successful seals or 5 W for 5 s for unsuccessful seals (control). All studies used a linear beam measuring 8.4 × 2.0 mm. Optical signals for successful and failed seals were correlated with vessel burst pressures (BP) using destructive testing via a standard BP setup. Light scattering increased significantly as vessels were coagulated. Successful seals correlated with a percent decrease in optical transmission signal of 59 ± 11 % and seal failures to a transmission decrease of 23 ± 8% (p < 0.01). With further development, the real-time optical feedback system may be integrated into a laparoscopic device to de-activate the laser upon successful vessel sealing.
Keywords: artery; blood vessel; coagulation; feedback; fusion; infrared; laser; seal; transmission.
Figures
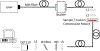

References
-
- Blencowe NS, Waldon R, and Vipond MN, “Management of patients after laparoscopic procedures,” BMJ, 360, k120 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Kennedy JS, Stranahan PL, Taylor KD, and Chandler JG, “High-burst-strength, feedback-controlled bipolar vessel sealing,” Surg. Endosc 12(6), 876–878 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Shigemura N, Akashi A, Nakagiri T, Ohta M, and Matsuda H, “A new tissue-sealing technique using LigaSure system for nonanatomical pulmonary resection: preliminary results of sutureless and stapleless thoracoscopic surgery,” Ann. Thorac. Surg 77(4), 1415–1418 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Patrone R, Gambardella C, Romano RM, Gugliemo C, Offi C, Andretta C, Vitiello A, Tartaglia E, Flagiello L, Conzo A, Mauriello C, and Conzo G, “The impact of the ultrasonic, bipolar and integrated energy devices in the adrenal gland surgery: literature review and our experience,” BMC Surg. 18 (Suppl 1), 123 (2019). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cilip CM, Rosenbury SB, Giglio NC, Hutchens TC, Schweinsberger GR, Kerr D, Latimer C, Nau WH, and Fried NM, “Infrared laser fusion of blood vessels: preliminary ex vivo tissue studies,” J. Biomed. Opt 18(5), 058001 (2013). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
