Does chronic kidney disease affect the complications and prognosis of patients after primary colorectal cancer surgery?
- PMID: 35949210
- PMCID: PMC9244980
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i6.1199
Does chronic kidney disease affect the complications and prognosis of patients after primary colorectal cancer surgery?
Abstract
Background: The effect of chronic kidney disease (CKD) on the outcomes of colorectal cancer (CRC) patients after primary CRC surgery is controversial.
Aim: To analyze whether CKD had specific effect on the outcomes after CRC surgery.
Methods: We searched the PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library databases and CNKI, from inception to March 14, 2022. Newcastle-Ottawa Scale was used for the quality assessment in this meta-analysis, and we used RevMan 5.3 was used for data analysis.
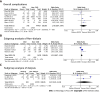
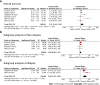
Results: A total of nine studies including 47771 patients were eligible for this meta-analysis. No significant difference was found in terms of overall postoperative complications [odds ratio (OR) = 1.78, 95%CI: 0.64-4.94, P = 0.27]. We analyzed the specific complications and found that the CKD group had higher rates of pulmonary infection (OR = 2.70, 95%CI: 1.82-4.00, P < 0.01), cardiovascular complications (OR = 3.39, 95%CI: 2.34-4.91, P < 0.01) and short-term death (OR = 3.01, 95%CI: 2.20-4.11, P < 0.01). After pooling the hazard ratio (HR), the CKD group had worse overall survival (OS) (HR = 1.51, 95%CI: 1.04-2.20, P = 0.03). We performed subgroup analyses of the dialysis and non-dialysis groups, and no significant difference was found in the non-dialysis group (HR = 1.20, 95%CI: 0.98-1.47, P = 0.08). The dialysis group had worse OS (HR = 3.36, 95%CI: 1.92-5.50, P < 0.01) than the non-dialysis group. The CKD group had worse disease-free survival (DFS) (HR = 1.41, 95%CI: 1.12-1.78, P < 0.01), and in the subgroup analysis of the dialysis and non-dialysis groups, no significant difference was found in the non-dialysis group (HR = 1.27, 95%CI: 0.97-1.66, P = 0.08). The dialysis group had worse OS (HR = 1.95, 95%CI: 1.23-3.10, P < 0.01) than the non-dialysis group.
Conclusion: Preexisting CKD was associated with higher rates of pulmonary infection, higher rates of short-term death, and worse OS and poorer DFS following CRC surgery.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Colorectal cancer; Meta-analysis; Outcome; Prognosis.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Bundred NJ. Erratum to "Impact of Oncotype DX Breast Recurrence Score testing on adjuvant chemotherapy use in early breast cancer: Real world experience in Greater Manchester, UK" [Eur J Surg Oncol 43 (5) (2017) 931-937] Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018;44:194. - PubMed
-
- Feliu J, Espinosa E, Basterretxea L, Paredero I, Llabrés E, Jiménez-Munárriz B, Antonio-Rebollo M, Losada B, Pinto A, Custodio AB, Del Mar Muñoz M, Gómez-Mediavilla J, Torregrosa MD, Soler G, Cruz P, Higuera O, Molina-Garrido MJ. Prediction of Chemotoxicity, Unplanned Hospitalizations and Early Death in Older Patients with Colorectal Cancer Treated with Chemotherapy. Cancers (Basel) 2021;14:127. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

