Dorsal Finger Fold Recognition by Convolutional Neural Networks for the Detection and Monitoring of Joint Swelling in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 35949225
- PMCID: PMC9247561
- DOI: 10.1159/000525061
Dorsal Finger Fold Recognition by Convolutional Neural Networks for the Detection and Monitoring of Joint Swelling in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
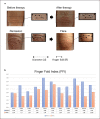
Digital biomarkers such as wearables are of increasing interest in monitoring rheumatic diseases, but they usually lack disease specificity. In this study, we apply convolutional neural networks (CNN) to real-world hand photographs in order to automatically detect, extract, and analyse dorsal finger fold lines as a correlate of proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint swelling in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Hand photographs of RA patients were taken by a smartphone camera in a standardized manner. Overall, 190 PIP joints were categorized as either swollen or not swollen based on clinical judgement and ultrasound. Images were automatically preprocessed by cropping PIP joints and extracting dorsal finger folds. Subsequently, metrical analysis of dorsal finger folds was performed, and a CNN was trained to classify the dorsal finger lines into swollen versus non-swollen joints. Representative horizontal finger folds were also quantified in a subset of patients before and after resolution of PIP swelling and in patients with disease flares. In swollen joints, the number of automatically extracted deep skinfold imprints was significantly reduced compared to non-swollen joints (1.3, SD 0.8 vs. 3.3, SD 0.49, p < 0.01). The joint diameter/deep skinfold length ratio was significantly higher in swollen (4.1, SD 1.4) versus non-swollen joints (2.1, SD 0.6, p < 0.01). The CNN model successfully differentiated swollen from non-swollen joints based on finger fold patterns with a validation accuracy of 0.84, a sensitivity of 88%, and a specificity of 75%. A heatmap of the original images obtained by an extraction algorithm confirmed finger folds as the region of interest for correct classification. After significant response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drug ± corticosteroid therapy, longitudinal metrical analysis of eight representative deep finger folds showed a decrease in the mean diameter/finger fold length (finger fold index, FFI) from 3.03 (SD 0.68) to 2.08 (SD 0.57). Conversely, the FFI increased in patients with disease flares. In conclusion, automated preprocessing and the application of CNN algorithms in combination with longitudinal metrical analysis of dorsal finger fold patterns extracted from real-world hand photos might serve as a digital biomarker in RA.
Keywords: Digital biomarker; Disease activity; Neural networks; Rheumatoid arthritis; Swelling.
Copyright © 2022 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Thomas Hügle is patentholder of DETECTRA. Thomas Hügle and Marc Blanchard are scientific board members of Atreon S.A.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Computer vision detects inflammatory arthritis in standardized smartphone photographs in an Indian patient cohort.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 9;10:1280462. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1280462. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38020147 Free PMC article.
-
Incorporating computer vision on smart phone photographs into screening for inflammatory arthritis: results from an Indian patient cohort.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2025 May 1;64(5):2525-2532. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae678. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2025. PMID: 39680895
-
Single-camera motion capture of finger joint mobility as a digital biomarker for disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2025 Apr 18;9(2):rkae143. doi: 10.1093/rap/rkae143. eCollection 2025. Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2025. PMID: 40256629 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis.Eur J Radiol. 1998 May;27 Suppl 1:S18-24. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(98)00038-2. Eur J Radiol. 1998. PMID: 9652497 Review.
-
[Swollen finger joints].MMW Fortschr Med. 2022 Oct;164(17):38-42. doi: 10.1007/s15006-022-1844-5. MMW Fortschr Med. 2022. PMID: 36198964 Review. German. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Implementation of a hybrid healthcare model in rheumatic musculoskeletal diseases: 6-months results of the multicenter Digireuma study.BMC Rheumatol. 2023 Sep 25;7(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s41927-023-00362-7. BMC Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37749656 Free PMC article.
-
Stepwise asynchronous telehealth assessment of patients with suspected axial spondyloarthritis: results from a pilot study.Rheumatol Int. 2024 Jan;44(1):173-180. doi: 10.1007/s00296-023-05360-z. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Rheumatol Int. 2024. PMID: 37316631 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of a hybrid telehealth care pathway for patients with axial spondyloarthritis including self-sampling at home: results of a longitudinal proof-of-concept mixed-methods study (TeleSpactive).Rheumatol Int. 2024 Jun;44(6):1133-1142. doi: 10.1007/s00296-024-05581-w. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Rheumatol Int. 2024. PMID: 38602534 Free PMC article.
-
Computer vision detects inflammatory arthritis in standardized smartphone photographs in an Indian patient cohort.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 9;10:1280462. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1280462. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38020147 Free PMC article.
-
Digitally-supported patient-centered asynchronous outpatient follow-up in rheumatoid arthritis - an explorative qualitative study.BMC Health Serv Res. 2022 Oct 28;22(1):1297. doi: 10.1186/s12913-022-08619-6. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022. PMID: 36307779 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Biomarkers Definition Working Group Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001;69((3)):89–95. - PubMed
-
- Pauk J, Trinkunas J, Puronaite R, Ihnatouski M, Wasilewska A. A computational method to differentiate rheumatoid arthritis patients using thermography data. Technol Health Care. 2022;30((1)):209–16. - PubMed
-
- Van der Heijde D, Boyesen P. Measuring disease activity and damage in arthritis. EULAR textbook on rheumatic diseases. 2012
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

