Drug costs in context: assessing drug costs in cost-of-illness analyses
- PMID: 35949272
- PMCID: PMC9333414
- DOI: 10.7573/dic.2022-5-4
Drug costs in context: assessing drug costs in cost-of-illness analyses
Abstract
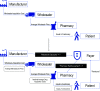
Cost-of-illness (COI) studies attempt to measure and describe the costs associated or attributed to a specific disease, but there are several considerations for measuring and interpreting drug costs estimates. The complexity of the pharmaceutical supply chain and contractual relationships between manufacturers, wholesalers, pharmacies and payers create challenges for researchers attempting to include drug costs in COI analyses. This article aims to provide contextual information for a general audience interested in conducting or evaluating COI studies that may include drug costs and to describe key factors to consider when reviewing drug costs in the peer-reviewed literature.
Keywords: burden-of-illness; cost-of-illness; drug costs; pharmacoeconomics.
Copyright © 2022 Mattingly II TJ, Weathers S.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and potential conflicts of interest: TJM reports consultant fees from the Arnold Foundation and PhRMA, all unrelated to this review. TJM also reports research grant support from PhRMA, the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute, and the Food and Drug Administration unrelated to this review. The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) Potential Conflicts of Interests form for the authors is available for download at: https://www.drugsincontext.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/dic.2022-5-4-COI.pdf
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-of-illness studies : a review of current methods.Pharmacoeconomics. 2006;24(9):869-90. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200624090-00005. Pharmacoeconomics. 2006. PMID: 16942122 Review.
-
Cost-of-illness studies. Useful for health policy?Pharmacoeconomics. 1998 Aug;14(2):143-8. doi: 10.2165/00019053-199814020-00001. Pharmacoeconomics. 1998. PMID: 10186453 Review.
-
Quantifying The Economic Burden Of Drug Utilization Management On Payers, Manufacturers, Physicians, And Patients.Health Aff (Millwood). 2021 Aug;40(8):1206-1214. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2021.00036. Health Aff (Millwood). 2021. PMID: 34339243
-
Cost-of-illness and disease burden of food-related pathogens in the Netherlands, 2011.Int J Food Microbiol. 2015 Mar 2;196:84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.11.022. Epub 2014 Dec 3. Int J Food Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25528537
-
Cost of lung cancer: a methodological review.Pharmacoeconomics. 2006;24(7):651-9. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200624070-00004. Pharmacoeconomics. 2006. PMID: 16802841 Review.
Cited by
-
Advanced Strategies in Enhancing the Hepatoprotective Efficacy of Natural Products: Integrating Nanotechnology, Genomics, and Mechanistic Insights.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025 May 12;11(5):2528-2549. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.5c00004. Epub 2025 Apr 11. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2025. PMID: 40211874 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Guideline on Country Pharmaceutical Pricing Policies. WHO Document Production Services; 2015. [Accessed July 11, 2022]. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/335692 . - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources