Tetratricopeptide repeat domain 9A knockout induces social anxiety and impairs offense behaviors in female mice
- PMID: 35949301
- PMCID: PMC9320210
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2022.63044.13932
Tetratricopeptide repeat domain 9A knockout induces social anxiety and impairs offense behaviors in female mice
Abstract
Objectives: The involvement of tetratricopeptide repeat domain 9A (TTC9A) in anxiety-like behaviors through estrogen action has been reported in female mice, this study further investigated its effects on social anxiety and aggressive behaviors.
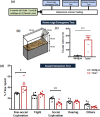
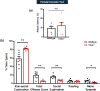
Materials and smethods: Using female Ttc9a knockout (Ttc9a-/-) mice, the role of TTC9A in anxiety was investigated in non-social and social environments through home-cage emergence and social interaction tests, respectively, whereas aggressive behaviors were examined under the female intruder test.
Results: We observed significant social behavioral deficits with pronounced social and non-social anxiogenic phenotypes in female Ttc9a-/- mice. When tested for aggressive-like behaviors, we found a reduction in offense in Ttc9a-/- animals, suggesting that TTC9A deficiency impairs the offense responses in female mice.
Conclusion: Future study investigating mechanisms underlying the social anxiety-like behavioral changes in Ttc9a-/- mice may promote the understanding of social and anxiety disorders.
Keywords: Aggression; Anxiety; Behavioral tests; Social behavior; Tetratricopeptide repeat - domain 9A (TTC9A).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Holt-Lunstad J, Smith TB, Baker M, Harris T, Stephenson D. Loneliness and social isolation as risk factors for mortality: a meta-analytic review. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2015;10:227–237. - PubMed
-
- Hakulinen C, Pulkki-Råback L, Virtanen M, Jokela M, Kivimäki M, Elovainio M. Social isolation and loneliness as risk factors for myocardial infarction, stroke and mortality: UK biobank cohort study of 479 054 men and women. Heart. 2018;104:1536–1542. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
