Thymoquinone-loaded mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome as an efficient nano-system against breast cancer cells
- PMID: 35949303
- PMCID: PMC9320205
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2022.64092.14116
Thymoquinone-loaded mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome as an efficient nano-system against breast cancer cells
Abstract
Objectives: Exosomes became the subject of extensive research in drug delivery approach due to their potential applicability as therapeutic tools for cancer therapy. Thymoquinone (Tq) is an anti-cancer agent due to its great anti-proliferative effect. However, poor solubility and weak bioavailability restrict its therapeutic applications. In this study, exosomes secreted from human adipocyte-derived mesenchymal stem cells (AdMSCs) were isolated and the efficacy of a novel encapsulation method for loading of Tq was investigated. Finally, the cytotoxic effect of Tq incorporated exosomes against cancer cells was evaluated.
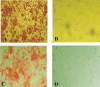
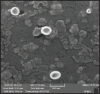
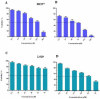
Materials and methods: Exosomes secreted from AdMSCs were isolated via ultracentrifugation and characterized by electron microscopy and western blotting. Then, through a novel encapsulation approach, Tq was loaded into exosomes by the combination of three methods including incubation, freeze-thawing, and surfactant treatment. Then, the encapsulation efficiency, in vitro cellular uptake, and cytotoxicity of Tq incorporated exosomes (Tq@EXOs) in MCF7 and L929 cells were estimated.
Results: Tq loading into exosomes through our novel method caused a significant improvement in encapsulation efficiency of about 60%. The fluorescent microscopy and flow cytometry outcomes indicated the efficient uptake of Tq@EXOs-FITC by cells throughout 4 hr. Furthermore, MTT results displayed the ability of Tq@EXOs in effectively decreasing the cell viability of MCF7 without causing any obvious cytotoxicity on L929 as normal cells.
Conclusion: The results suggest that our approach provides effective loading of Tq into exosomes which offer a valuable and safe platform for drug delivery to cancer cells thus having a great potential for clinical studies.
Keywords: Adipose-derived; Breast cancer; Drug delivery system; Exosome; Thymoquinone; mesenchymal; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Co-encapsulation of thymoquinone with docetaxel enhances the encapsulation efficiency into PEGylated liposomes and the chemosensitivity of MCF7 breast cancer cells to docetaxel.Heliyon. 2019 Nov 27;5(11):e02919. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02919. eCollection 2019 Nov. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31844767 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of 5-fluorouracil, thymoquinone, and mammary stem cells' exosomes on in vitro cultured breast cancer cells.Open Vet J. 2024 Jan;14(1):525-533. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i1.47. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Open Vet J. 2024. PMID: 38633189 Free PMC article.
-
Thymoquinone-treated mouse mesenchymal stem cells-derived conditioned medium inhibits human breast cancer cells in vitro.Chem Biol Interact. 2023 Jan 5;369:110283. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110283. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Chem Biol Interact. 2023. PMID: 36450322
-
The Influence of Pluronic F68 and F127 Nanocarrier on Physicochemical Properties, In vitro Release, and Antiproliferative Activity of Thymoquinone Drug.Pharmacognosy Res. 2017 Jan-Mar;9(1):12-20. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.199774. Pharmacognosy Res. 2017. PMID: 28250648 Free PMC article.
-
Nanocarriers: more than tour de force for thymoquinone.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020 Apr;17(4):479-494. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2020.1730808. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32077770 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineered Exosome for Drug Delivery: Recent Development and Clinical Applications.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Dec 23;18:7923-7940. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S444582. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 38152837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential of Exosomes as Multifunctional Nanocarriers for Targeted Drug Delivery.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Sep 13. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01268-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39269575 Review.
-
Research Advances of Engineered Exosomes as Drug Delivery Carrier.ACS Omega. 2023 Nov 9;8(46):43374-43387. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c04479. eCollection 2023 Nov 21. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38027310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amphotericin B-Loaded Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Leishmania major Enhancing Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Treatment through In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Iran J Parasitol. 2023 Oct-Dec;18(4):514-525. doi: 10.18502/ijpa.v18i4.14260. Iran J Parasitol. 2023. PMID: 38169565 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury.Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2024;12(6):380-399. doi: 10.22038/ABJS.2023.73944.3424. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2024. PMID: 38919744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pullan JE, Confeld MI, Osborn JK, Kim J, Sarkar K, Mallik S. Exosomes as drug carriers for cancer therapy. Mol Pharm. 2019;5:1789–1798. - PubMed
-
- Clayton A, Turkes A, Dewitt S, Steadman R, Mason MD, Hallett MB. Adhesion and signaling by B cell-derived exosomes: the role of integrins. FASEB J. 2004;9:977–979. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
