Exploration of autonomic regulation reflecting on pathophysiological change of sepsis: a prospective observational study
- PMID: 35949315
- PMCID: PMC9353857
- DOI: 10.1002/ams2.776
Exploration of autonomic regulation reflecting on pathophysiological change of sepsis: a prospective observational study
Abstract
Aim: It remains unclear how autonomic regulation modulates pathophysiological changes of sepsis. This study aims to analyze and clarify those in patients with suspected sepsis.
Methods: In this single-centered, prospective, observational study, adult patients who had an infection, a quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score of 2 or more at the emergency department, and underwent intensive care were screened. Heart rate variability (HRV) and serum adrenaline were measured immediately after arrival. The primary outcome was defined as vasopressor dependence during 48 h after arrival.
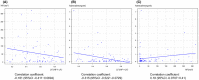
Results: A total of 63 patients were included. All the patients had SOFA score of 2 or more on admission. Vasopressor dependence, renal replacement therapy, and in-hospital mortality were associated with higher adrenaline (which reflects sympathetic adrenergic system activity). Bacteremia was associated with lower high-frequency components of HRV (parasympathetic nerve activity). The HRV parameter of sympathetic nerve activity had no significant association with the outcomes. In the multivariate logistic regression model adjusted for age and sex, vasopressor dependence remained associated with higher adrenaline (cut-off 0.11 ng/mL, odds ratio 9.71, 95% confidence interval 2.55-37; P = 0.000874), and lower high-frequency components with bacteremia (17.2 ms2, odds ratio 4.86, 95% confidence interval 1.36-17.4; P = 0.0152). There were no significant correlations between parameters of HRV and serum adrenaline.
Conclusion: Hypoperfusion, organ dysfunction, and in-hospital mortality were associated with an increased sympathetic adrenergic activity. Bacteremia was associated with decreased parasympathetic nerve activity. The autonomic regulator may involve a multilayered and differentiated modulating process for sepsis.
Keywords: Adrenaline; autonomic nervous system; bacteremia; sepsis; septic shock.
© 2022 The Authors. Acute Medicine & Surgery published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Association for Acute Medicine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Combined prognostic value of serum lactic acid, procalcitonin and severity score for short-term prognosis of septic shock patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Mar;33(3):281-285. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20201113-00715. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 33834968 Chinese.
-
Initial fractal exponent of heart rate variability is associated with success of early resuscitation in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock: a prospective cohort study.J Crit Care. 2013 Dec;28(6):959-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2013.07.050. Epub 2013 Aug 17. J Crit Care. 2013. PMID: 23958243 Free PMC article.
-
Multicenter observational study of the development of progressive organ dysfunction and therapeutic interventions in normotensive sepsis patients in the emergency department.Acad Emerg Med. 2013 May;20(5):433-40. doi: 10.1111/acem.12137. Acad Emerg Med. 2013. PMID: 23672356
-
Monitoring circulating dipeptidyl peptidase 3 (DPP3) predicts improvement of organ failure and survival in sepsis: a prospective observational multinational study.Crit Care. 2021 Feb 15;25(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03471-2. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33588925 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score As a Predictor of Outcome in Sepsis in Pediatric Intensive Care Unit.J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2021 Jun;10(2):110-117. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1714705. Epub 2020 Jul 30. J Pediatr Intensive Care. 2021. PMID: 33884211 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marrero MB, Bencherif M. Convergence of alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor‐activated pathways for anti‐apoptosis and anti‐inflammation: central role for JAK2 activation of STAT3 and NF‐kappaB. Brain Res. 2009; 1256: 1–7. - PubMed
-
- Schwencke C, Schmeisser A, Weinbrenner C, Braun‐Dullaeus RC, Marquetant R, Strasser RH. Transregulation of the alpha2‐adrenergic signal transduction pathway by chronic beta‐blockade: a novel mechanism for decreased platelet aggregation in patients. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2005; 45: 253–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

