Risk factors for lymph node metastasis in patients with pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms
- PMID: 35949434
- PMCID: PMC9244965
- DOI: 10.5306/wjco.v13.i6.520
Risk factors for lymph node metastasis in patients with pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms
Abstract
Background: Although PNENs generally have a better prognosis than pancreatic cancers, some PNENs display malignant behavior including lymph node (LN) metastasis. Complete tumor resection can be the only potentially curative treatment for patients with resectable PNENs. However, the indications for LN dissection are still controversial. Over the last decade, minimally invasive surgery such as laparoscopic pancreatic surgery (LPS) has been increasingly performed for pancreatic tumors including PNENs.
Aim: To investigate the risk factors for LN metastasis in PNENs and to select appropriate patients for limited surgery by LPS.
Methods: From April 2001 to December 2019, 92 patients underwent pancreatic resection for PNENs at Kumamoto University Hospital. Finally, 82 patients were enrolled in this study. Using perioperative factors, we examined the predictive factors for LN metastasis in PNENs.
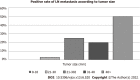
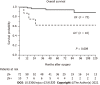
Results: Among the 82 patients, the percentage of LN metastasis according to the pathological findings was 12% (10/82 cases). The median tumor size was 12 mm (range: 5-90 mm). The median tumor size in the LN-positive group (37 mm) was significantly larger than that in the LN-negative group (12 mm) (P = 0.0001). Multivariate analyses revealed that larger tumor size (≥ 20 mm) was an independent risk factor for LN metastasis (odds ratio 16.8, P = 0.0062). In patients with small tumors (≤ 10 mm), LN metastasis was not found.
Conclusion: Larger tumor size (≥ 20 mm) is an independent risk factor for LN metastasis in PNENs. In smaller PNENs (≤ 10 mm), we may be able to choose limited surgery without LN dissection.
Keywords: Lymph node metastasis; Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms; Risk factor; Tumor size.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All the authors have no conflicts of interest in association with this study. No financial support was received for the work described in this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The associations between serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and malignant behavior in pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms.Lipids Health Dis. 2022 Jul 16;21(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12944-022-01669-z. Lipids Health Dis. 2022. PMID: 35842659 Free PMC article.
-
Malignant potential of small pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasm and its risk factors: A multicenter nationwide study.Pancreatology. 2021 Jan;21(1):208-214. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.11.016. Epub 2020 Dec 1. Pancreatology. 2021. PMID: 33281058
-
Comparison of prognosis between observation and surgical resection groups with small sporadic non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms without distant metastasis.J Gastroenterol. 2020 May;55(5):543-552. doi: 10.1007/s00535-019-01655-w. Epub 2019 Dec 19. J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 31858231
-
Update on surgical treatment of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Oct 14;20(38):13893-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13893. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25320524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Surgery of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms: state of the art].Chirurgie (Heidelb). 2022 Aug;93(8):745-750. doi: 10.1007/s00104-022-01641-8. Epub 2022 May 2. Chirurgie (Heidelb). 2022. PMID: 35499762 Review. German.
Cited by
-
New nomogram for predicting lymph node positivity in pancreatic head cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 25;13:1053375. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1053375. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36761960 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: Beyond Traditional Surgery and Targeted Therapy.J Clin Med. 2025 May 13;14(10):3389. doi: 10.3390/jcm14103389. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40429384 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yao JC, Hassan M, Phan A, Dagohoy C, Leary C, Mares JE, Abdalla EK, Fleming JB, Vauthey JN, Rashid A, Evans DB. One hundred years after "carcinoid": epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3063–3072. - PubMed
-
- Fischer L, Bergmann F, Schimmack S, Hinz U, Prieß S, Müller-Stich BP, Werner J, Hackert T, Büchler MW. Outcome of surgery for pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Br J Surg. 2014;101:1405–1412. - PubMed
-
- Kleine M, Schrem H, Vondran FW, Krech T, Klempnauer J, Bektas H. Extended surgery for advanced pancreatic endocrine tumours. Br J Surg. 2012;99:88–94. - PubMed
-
- Asbun HJ, Stauffer JA. Laparoscopic vs open pancreaticoduodenectomy: overall outcomes and severity of complications using the Accordion Severity Grading System. J Am Coll Surg. 2012;215:810–819. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

