Role of circular RNAs in the diagnosis, regulation of drug resistance and prognosis of lung cancer
- PMID: 35949591
- PMCID: PMC9353231
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2022.13422
Role of circular RNAs in the diagnosis, regulation of drug resistance and prognosis of lung cancer
Abstract
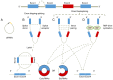
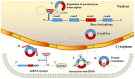
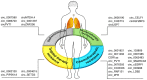
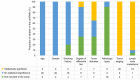
Lung cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors in China and is the highest cause of mortality among male and female patients, both in urban and rural areas. A subset of patients with lung cancer only display chest tightness without any other obvious symptoms. This is because most symptoms do not manifest during the early stages of disease development. Consequently, most patients with lung cancer are diagnosed when the disease is in the advanced stages, when they are already unfit for surgical treatment. Furthermore, the prognosis of patients with lung cancer is poor. The 5-year survival rate of patients with stage IA lung cancer is 85%, compared with 6% in those with stage IV. This requires the development of strategies for early diagnosis, treatment and prognosis to improve the management of lung cancer. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) belong to a class of closed circular non-coding RNAs formed by reverse splicing of a precursor mRNA. These RNAs are highly stable, ubiquitously expressed, conserved, and show high specificity. CircRNAs regulate biological processes, such as the proliferation, differentiation and invasion of lung cancer cells. Therefore, they can be used as biomarkers for the early diagnosis and prognosis prediction of lung cancer, as well as novel targets for therapy design. In the present review, the biological characteristics and functions of circRNAs, as well as their application in the diagnosis, control of drug resistance and effect on the prognosis of patients with lung cancer, will be discussed.
Keywords: circular RNAs; diagnosis; drug resistance; lung cancer; prognosis.
Copyright: © Sang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circular RNAs as biomarkers for lung cancer.Noncoding RNA Res. 2022 Nov 7;8(1):83-88. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2022.11.002. eCollection 2023 Mar. Noncoding RNA Res. 2022. PMID: 36407660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mechanism and Clinical Significance of Circular RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 2;11:714665. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.714665. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34540684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircRNAs and lung cancer: Biomarkers and master regulators.Life Sci. 2019 Mar 1;220:177-185. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.01.055. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30711537 Review.
-
Clinical Implications of Circulating Circular RNAs in Lung Cancer.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 8;10(4):871. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040871. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35453621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CircRNAs in lung cancer - Biogenesis, function and clinical implication.Cancer Lett. 2020 Nov 1;492:106-115. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.08.013. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 32860847 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Insights into the Angioregulatory Role of Long Non-coding RNAs and Circular RNAs in Gliomas: From Signaling Pathways to Clinical Aspects.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(16):3169-3192. doi: 10.2174/0109298673259378231031061149. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 38258785 Review.
-
The role of circular RNAs in regulating resistance to cancer immunotherapy: mechanisms and implications.Cell Death Dis. 2024 May 2;15(5):312. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06698-3. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38697964 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
