Magnetic resonance imaging and intractable epilepsy: A systematic review
- PMID: 35949699
- PMCID: PMC9288133
Magnetic resonance imaging and intractable epilepsy: A systematic review
Abstract
Objective: Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that occurs due to irregular neuronal activity in the central nervous system. The main job of a radiologist is to investigate the structural etiology in epilepsy patients. This study was undertaken to find out the importance of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in the screening of intractable epilepsy through a systematic search of literature.
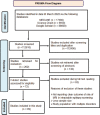
Methods: A systematic review was performed using the PRISMA guidelines. Peer-reviewed studies on MRI and intractable epilepsy were retrieved from MEDLINE, ScienceDirect and Google Scholar. Moreover, studies cited in the key articles were also screened to increase the sensitivity and specificity of the systematic search.
Results: The database search till March 2022 found a total of 112610 articles. Out of them, only 10 highly selected articles were included in the study. The pooled data point out that the rapid development in MRI techniques and the functional MRI (fMRI) has now become more and more critical in the diagnosis and management of patients with epilepsy. In addition, the data also pointed out that MRI-based approaches are also very useful for post-operative epilepsy patients as it gives information about the quality of the surgery. The data collected showed that the MRI is the choice technique for the evaluation of patients with epilepsy.
Conclusions: The applicability of MRI in epilepsy diagnosis is highly accessible in all over the globe. The pooled data concluded that the MRI-based surgical approaches are extremely useful for the surgeons to provide three-dimensional imaging with superimposed real-time pointer details that have proved successful for epilepsy patients.
Keywords: MRI; functional MRI; intractable epilepsy; systematic review.
Copyright: © International Journal of Health Sciences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Surgery for epilepsy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jun 25;6(6):CD010541. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010541.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31237346 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(12):1-38. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074389 Free PMC article.
-
Correlating Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Connectivity by Independent Component Analysis-Based Epileptogenic Zones with Intracranial Electroencephalogram Localized Seizure Onset Zones and Surgical Outcomes in Prospective Pediatric Intractable Epilepsy Study.Brain Connect. 2017 Sep;7(7):424-442. doi: 10.1089/brain.2016.0479. Brain Connect. 2017. PMID: 28782373 Free PMC article.
-
Investigatory pathway and principles of patient selection for epilepsy surgery candidates: a systematic review.BMC Neurol. 2020 Mar 17;20(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12883-020-01680-w. BMC Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32183734 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Devinsky O, Vezzani A, O'Brien TJ, Jette N, Scheffer IE, De Curtis M, et al. Epilepsy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18024. - PubMed
-
- Espinosa-Jovel C, Toledano R, Aledo-Serrano Á, García-Morales I, Gil-Nagel A. Epidemiological profile of epilepsy in low income populations. Seizure. 2018;56:67–72. - PubMed
-
- Carpio A, Hauser WA. Epilepsy in the developing world. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2009;9:319–26. - PubMed
-
- Newton CR, Garcia HH. Epilepsy in poor regions of the world. Lancet. 2012;380:1193–201. - PubMed
-
- Singh G, Sander JW. The global burden of epilepsy report:Implications for low- and middle-income countries. Epilepsy Behav. 2020;105:106949. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources