The Diagnostic Value of GGT-Based Biochemical Indicators for Choledocholithiasis with Negative Imaging Results of Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography
- PMID: 35949700
- PMCID: PMC9348969
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7737610
The Diagnostic Value of GGT-Based Biochemical Indicators for Choledocholithiasis with Negative Imaging Results of Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography
Abstract
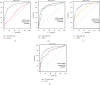
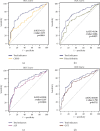
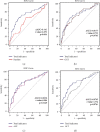
To reveal the relationship between a group of preoperative biochemical indicators such as GGT, ALP, ALT, AST, TB, and DB and the occurrence of common bile duct stones in patients with negative results of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, a retrospective diagnostic accuracy clinical test is conducted in this study. In order to reduce the missed diagnosis rate of choledocholithiasis and perform more accurate common bile duct exploration, 466 patients who underwent surgical treatment of cholelithiasis from January 2014 to December 2015 have been analyzed retrospectively. Firstly, the confounding factors are corrected through Binary Logistic regression. Then, the diagnostic efficacy of each indicator is measured by the ROC curve among different types of patients. In all patients, the top three individual indicators with the greatest AUC curve area for predicting common bile duct stones can be observed from the results of MRCP, γ-glutamyl transpeptidase, and alkaline phosphatase. Besides, the diagnostic efficiency of the comprehensive evaluation is higher than that of all individual indicators. For MRCP-negative patients, the top three largest AUC curve area of the diagnostic efficacy for choledocholithiasis were GGT, ALP, and DB. For patients who have a suspected diagnosis of secondary choledocholithiasis, the diagnostic efficacy of the combination of imaging results, biochemical indexes, common bile duct width, and other abnormal indicators for choledocholithiasis is much higher than that of the single abnormal biochemical indexes for the prediction of choledocholithiasis. For MRCP-negative patients, GGT, ALP, DB, and the width of common bile duct diameter are valuable for the prediction of common bile duct stones, and GGT is the most valuable diagnostic predictor.
Copyright © 2022 Huajun Lin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kim S. Y., Kim K. H., Kim I. D., et al. The variation of hepatic duct confluence and asymptomatic common bile duct stone with routine intraoperative cholangiogram during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Korean Journal of Gastroenterology . 2011;58(6):338–345. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2011.58.6.338. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kim H., Shin S. P., Hwang J. W., Lee J. W. Outcomes of laparoscopic common bile duct exploration (LCBDE) after failed endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography versus primary LCBDE for managing cholecystocholedocholithiasis. Journal of International Medical Research . 2020;48(10) doi: 10.1177/0300060520957560.030006052095756 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
