Paclitaxel-Induced Pneumonitis in Trinidad: A Case Report
- PMID: 35949737
- PMCID: PMC9357421
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.26613
Paclitaxel-Induced Pneumonitis in Trinidad: A Case Report
Abstract
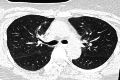
Paclitaxel-induced pneumonitis (PIP) is an immune-mediated disease resulting from a delayed hypersensitivity reaction (type IV) to paclitaxel, an anti-microtubule chemotherapeutic drug commonly used to treat breast cancer in both neoadjuvant and adjuvant settings. PIP is diagnosed by exclusion utilizing laboratory work-up, imaging, biopsy studies, and results of antibiotic therapy because there is no single diagnostic test. Ground-glass opacifications on CT, coupled with minimal restrictive disturbance with decreased diffusion on pulmonary function tests (PFTs), negative bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), and bronchoscopy cultures, may assist physicians in diagnosing paclitaxel-induced pneumonitis. In this report, we describe a case of PIP present in Trinidad, West Indies, which has not been described previously in this region.
Keywords: breast cancer; drug-induced; hypersensitivity; paclitaxel; pneumonitis.
Copyright © 2022, Mohan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bird fancier's lung: a series of 86 patients.Medicine (Baltimore). 2008 Mar;87(2):110-130. doi: 10.1097/MD.0b013e31816d1dda. Medicine (Baltimore). 2008. PMID: 18344808
-
Paclitaxel-induced cell-mediated hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Diagnosis using leukocyte migration test, bronchoalveolar lavage and transbronchial lung biopsy.Oncology. 1998 Jul-Aug;55(4):340-4. doi: 10.1159/000011873. Oncology. 1998. PMID: 9663424
-
Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis in patients diagnosed with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a prospective case-cohort study.Lancet Respir Med. 2013 Nov;1(9):685-94. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(13)70191-7. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Lancet Respir Med. 2013. PMID: 24429272
-
[A case of paclitaxel-induced pneumonitis].Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2004 Feb;42(2):158-63. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15007916 Review. Japanese.
-
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis reaction to Mycobacterium avium in household water.Chest. 2005 Feb;127(2):664-71. doi: 10.1378/chest.127.2.664. Chest. 2005. PMID: 15706013 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK pathways attenuates Golgi tethering factor golgin-97 depletion-induced cancer progression in breast cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jan 13;23(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-02010-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 39800687 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pulmonary complications of novel antineoplastic agents for solid tumors. Vahid B, Marik PE. Chest. 2008;133:528–538. - PubMed
-
- Paclitaxel-induced pneumonitis in patients with breast cancer: case series and review of the literature. Bielopolski D, Evron E, Moreh-Rahav O, Landes M, Stemmer SM, Salamon F. J Chemother. 2017;29:113–117. - PubMed
-
- Drug-induced infiltrative lung disease with weekly paclitaxel in breast cancer: case series. Raghupathi R, Patil C, Dhiman P. https://www.cancerjournal.net/article.asp?issn=0973-1482;year=2021;volum.... J Cancer Res Ther. 2021;17:262–265. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources