A Novel Physical Therapy Approach in Pain Management and Enhancement of Performance in Shin Splints Athletes: A Case Report
- PMID: 35949752
- PMCID: PMC9358988
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.26676
A Novel Physical Therapy Approach in Pain Management and Enhancement of Performance in Shin Splints Athletes: A Case Report
Abstract
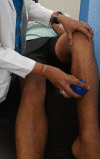
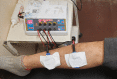
Runners are most commonly attributed to the shin splint, which is showing commonly the symptom of leg pain. It may be misdiagnosed as compartment syndrome as well. This case report depicts the standard condition of medial tibial stress syndrome in a long-distance runner, which is an acute condition with worsening symptoms in many authors' opinion. Patients with accurate symptoms of the conditions may be diagnosed with shin splints for medical usage. Only pain along the posterior medial border of the tibia at the origin of the posterior tibialis muscle should be referred to as shin splints. The chronic form of anterior compartment syndrome may attribute to the runner if they ignore the symptoms of leg pain that occurs in shin splints. Anterior tibial pain during activity is frequent in athletes. It has been linked to various disorders, including periostitis from improper stretching and muscular conditioning, as well as exertional compartment syndromes.
Keywords: athletic condition; conservative management; cupping therapy; pain and function; shin splints.
Copyright © 2022, Deshmukh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Anterior compartment syndrome: a case report. Pearl AJ. Am J Sports Med. 1981;9:119–120. - PubMed
-
- Exercise related leg pain (ERLP): a review of the literature. Reinking MF. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2953294/ N Am J Sports Phys Ther. 2007;2:170–180. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Relieving painful 'shin splints'. Fick DS, Albright JP, Murray BP. Phys Sportsmed. 1992;20:105–113. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources