Spontaneous Escherichia coli Empyema Thoracis: An Unusual Occurrence in a Non-cirrhotic, Immunocompetent Individual
- PMID: 35949758
- PMCID: PMC9356649
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.26618
Spontaneous Escherichia coli Empyema Thoracis: An Unusual Occurrence in a Non-cirrhotic, Immunocompetent Individual
Abstract
Spontaneous bacterial empyema is a spontaneous infection of the pleural cavity in the absence of pneumonia, typically seen in patients with liver cirrhosis and preexisting hepatic hydrothorax. Empyema thoracis caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a rare clinical finding and, in most cases, a consequence of E. coli pneumonia. Spontaneous bacterial empyema secondary to E. coli in a non-cirrhotic individual is an unusual association, rarely described in the literature. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of spontaneous bacterial E. coli empyema thoracis in a non-cirrhotic, immunocompetent individual with a complex medical history including pulmonary thromboembolism, oropharyngeal dysphagia, and a high aspiration risk of oropharyngeal secretions.
Keywords: complex medical history; escherichia coli empyema; high aspiration risk; non-cirrhotic; oropharyngeal dysphagia; pulmonary thromboembolism; spontaneous bacterial empyema.
Copyright © 2022, Sabir et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


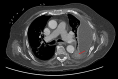
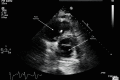
References
-
- Empyema thoracis: new insights into an old disease. Brims FJ, Lansley SM, Waterer GW, Lee YC. https://doi.org/10.1183/09059180.00005610. Eur Respir Rev. 2010;19:220–228. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pleural empyema. Bryant RE, Salmon CJ. https://doi.org/10.1093/clinids/22.5.747. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;22:747–764. - PubMed
-
- Aerobic and anaerobic microbiology of empyema: a retrospective review in two military hospitals. Brook I, Frazier EH. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.103.5.1502. Chest. 1993;103:1502–1507. - PubMed
-
- Empyema thoracis. Ahmed AE, Yacoub TE. https://doi.org/10.4137/ccrpm.s5066. Clin Med Insights Circ Respir Pulm Med. 2010;4:1–8. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
