Expression and prognostic potential of TMEM204: a pan-cancer analysis
- PMID: 35949807
- PMCID: PMC9360586
Expression and prognostic potential of TMEM204: a pan-cancer analysis
Abstract
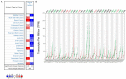
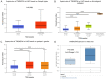
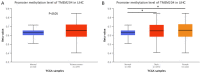
TMEM204 (Transmembrane Protein 204) is a member of the TMEM family that regulates cell function and angiogenesis. Previous studies showed that TMEM204 is related to pancreatic cancer, but its roles in other cancers remain unknown. To reveal this relationship, we conducted a pan-cancer analysis by several online databases. The expression of TMEM204 was analyzed by Oncomine and Tumor Immune Estimation Resource2.0 (TIMER2.0). The prognostic potential of TMEM204 was evaluated by the GEPIA2, UALCAN, and Oncolnc. The methylation level of gene expression was analyzed by UALCAN, and the relationship between cancer and immune invasion was displayed by TIMER2.0. The Protein-Protein Interactions Network and functional analysis of TMEM204 and its related genes were conducted by STRING and Webgestalt. We found that TMEM204 expression was up-regulated and correlated with prognosis in multiple cancers. In liver hepatocellular carcinoma (LIHC), high TMEM204 expression was associated with a good prognosis, and with high infiltrating levels of CD8+ T and CD4+ T cells, macrophages, neutrophils, and myeloid dendritic cells. In addition, the methylation level in LIHC was higher than in normal tissues. p53 signaling pathway and Fanconi anemia pathway were implicated by KEGG pathway analysis. These results indicate that TMEM204 is associated with the prognosis, methylation, and immune invasion of cancers, especially LIHC. TMEM204 may act as a prognostic marker of LIHC and its role in other cancers should be studied.
Keywords: Expression; TMEM204; methylation; pan-cancer analysis; prognostic biomarker.
IJCEP Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




Similar articles
-
FIGNL1 Expression and its Prognostic Significance in Pan-cancer Analysis.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022;25(13):2180-2190. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666220301110517. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022. PMID: 35232348
-
E2F1 as a potential prognostic and therapeutic biomarker by affecting tumor development and immune microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 Aug;11(8):2713-2732. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-218. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36093522 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value and immunological role of BAIAP2L2 in liver hepatocellular carcinoma: A pan-cancer analysis.Front Surg. 2022 Oct 21;9:985034. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.985034. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 36338652 Free PMC article.
-
BRCA1-Associated Protein Is a Potential Prognostic Biomarker and Is Correlated With Immune Infiltration in Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Pan-Cancer Analysis.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Nov 2;7:573619. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.573619. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33240929 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Therapeutic Targets and Prognostic Biomarkers Among Chemokine (C-C Motif) Ligands in the Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma Microenvironment.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Dec 6;9:748269. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.748269. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34938730 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparative Transcriptome Profiles of Human HaCaT Cells in Response to Gynostemma pentaphyllum Extracts Obtained Using Three Independent Methods by RNA Sequencing.Life (Basel). 2023 Feb 2;13(2):423. doi: 10.3390/life13020423. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836780 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of transmembrane proteins in tumorigenesis and therapy.Transl Cancer Res. 2025 Feb 28;14(2):1447-1466. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-1660. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Transl Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40104699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TMEM147 Correlates with Immune Infiltration and Serve as a Potential Prognostic Biomarker in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2023 Jun 3;2023:4413049. doi: 10.1155/2023/4413049. eCollection 2023. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2023. PMID: 37305689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Yan P, Wang P, Liu LH. Sonodynamic Therapy (SDT) for cancer treatment: advanced sensitizers by ultrasound activation to injury tumor. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020;3:3456–3475. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–386. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
