Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in comparison to infliximab for Crohn's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35949827
- PMCID: PMC9254215
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i18.6091
Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in comparison to infliximab for Crohn's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Adalimumab (ADA) and infliximab (IFX) are the cornerstones of the treatment of Crohn's disease (CD). It remains controversial whether there is a difference in the effectiveness and safety between IFX and ADA for CD.
Aim: To perform a meta-analysis to compare the effectiveness and safety of ADA and IFX in CD.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases were searched. Cohort studies were considered for inclusion. The primary outcomes were induction of response and remission, maintenance of response and remission, and secondary loss of response. Adverse events were secondary outcomes.
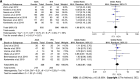
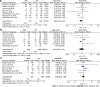
Results: Fourteen cohort studies were included. There was no apparent difference between the two agents in the induction response [odds ratio (OR): 1.27, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.93-1.74, P = 0.14] and remission (OR: 1.11, 95%CI: 0.78-1.57, P = 0.57), maintenance response (OR: 1.08, 95%CI: 0.76-1.53, P = 0.67) and remission (OR: 1.26, 95%CI: 0.87-1.82, P = 0.22), and secondary loss of response (OR: 1.01, 95%CI: 0.65-1.55, P = 0.97). Subgroup analysis revealed ADA and IFX had similar rates of response, remission, and loss of response either in anti-tumor necrosis factor-α naïve or non-naïve patients. Further, there was a similar result regardless of whether CD patients were treated with optimized therapy, including dose intensification, shortening interval, and combination immunomodulators. However, ADA had a fewer overall adverse events than IFX (OR: 0.62, 95%CI: 0.42-0.91, P = 0.02).
Conclusion: ADA and IFX have similar clinical benefits for anti-tumor necrosis factor-α naïve or non-naïve CD patients. Overall adverse events rate is higher in patients in the IFX group.
Keywords: Adalimumab; Adverse effects; Clinical efficacy; Crohn disease; Infliximab; Meta-analysis.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Nothing to disclosed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Efficacy and Safety of Infliximab Versus Adalimumab in Adult Subjects With Moderate to Severe Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Jun 2;16(6):e61547. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61547. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38835557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Effectiveness of Infliximab Versus Adalimumab in Patients with Biologic-Naïve Crohn's Disease.Dig Dis Sci. 2018 May;63(5):1302-1310. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4874-6. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Dig Dis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29243105
-
The efficacy and safety of either infliximab or adalimumab in 362 patients with anti-TNF-α naïve Crohn's disease.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Jul;44(2):170-80. doi: 10.1111/apt.13671. Epub 2016 May 26. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27226407
-
Long-Term Clinical Remission in Biologically Naïve Crohn's Disease Patients with Adalimumab Therapy, Including Analyses of Switch from Adalimumab to Infliximab.Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2016 Jun 14;10(2):283-91. doi: 10.1159/000445105. eCollection 2016 May-Aug. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27462198 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in pediatric patients with Crohn's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Mar;80(3):395-407. doi: 10.1007/s00228-023-03613-1. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38157000 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biologics for Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Clinical Practice: A Calabria (Southern Italy) Prospective Pharmacovigilance Study.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Nov 13;14(11):2449. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14112449. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36432640 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Efficacy of Subcutaneous Versus Intravenous Interleukin 12/23 Inhibitors for the Remission of Moderate to Severe Crohn's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Biomedicines. 2025 Mar 12;13(3):702. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13030702. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40149677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A case of pulmonary and cutaneous sarcoidosis.Breathe (Sheff). 2025 Apr 17;21(2):240228. doi: 10.1183/20734735.0228-2024. eCollection 2025 Apr. Breathe (Sheff). 2025. PMID: 40255295 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Infliximab Versus Adalimumab in Adult Subjects With Moderate to Severe Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Jun 2;16(6):e61547. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61547. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38835557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Narrative review of adalimumab for the treatment of cardiac sarcoidosis.Heart Rhythm O2. 2025 Jan 9;6(3):368-382. doi: 10.1016/j.hroo.2024.12.012. eCollection 2025 Mar. Heart Rhythm O2. 2025. PMID: 40201681 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Danese S, Vuitton L, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Biologic agents for IBD: practical insights. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;12:537–545. - PubMed
-
- Singh S, Garg SK, Pardi DS, Wang Z, Murad MH, Loftus EV Jr. Comparative efficacy of biologic therapy in biologic-naïve patients with Crohn disease: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014;89:1621–1635. - PubMed
-
- Kestens C, van Oijen MG, Mulder CL, van Bodegraven AA, Dijkstra G, de Jong D, Ponsioen C, van Tuyl BA, Siersema PD, Fidder HH, Oldenburg B Dutch Initiative on Crohn and Colitis (ICC) Adalimumab and infliximab are equally effective for Crohn's disease in patients not previously treated with anti-tumor necrosis factor-α agents. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:826–831. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

