Clivus-involved immunoglobulin G4 related hypertrophic pachymeningitis mimicking meningioma: A case report
- PMID: 35949844
- PMCID: PMC9254204
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i18.6269
Clivus-involved immunoglobulin G4 related hypertrophic pachymeningitis mimicking meningioma: A case report
Abstract
Background: Immunoglobulin G4 related disease (IgG4-RD) is a fibroinflammatory disease with markedly elevated serum IgG4 levels and fibrous tissue proliferation, accompanied by numerous plasma cells. IgG4 related hypertrophic pachymeningitis (IgG4-RHP) is relatively rare and indistinguishable from other phymatoid diseases before the operation. The risk of long-term immunosuppression needs to be balanced with disease activity.
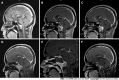
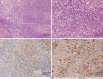
Case summary: A 40-year-old man presented with headache and bilateral abducent paralysis. He was also diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis 10 years ago and was on regular treatment for the same. Before the operation and steroid therapy, the patient was suspected of having tubercular meningitis at a local hospital. A clivus lesion was found via brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at this presentation. He was preliminarily diagnosed with meningioma and underwent Gamma Knife Surgery. Transnasal endoscopic resection was performed to treat deterioration of nerve function. Postoperative pathologic examination suggested IgG4-RD. Moreover, the serum IgG4 was elevated at 1.90 g/L (reference range: 0.035-1.500 g/L). After steroid therapy for 2 mo, the lesion size diminished on MRI, and the function of bilateral abducent nerves recovered.
Conclusion: IgG4-RHP is relatively rare and indistinguishable before the operation. Elevated serum IgG4 levels and imaging examination help in the diagnosis of IgG4-RHP. Surgery is necessary when lesions progress and patients start to develop cranial nerve function deficit.
Keywords: Case report; Clivus; Hypertrophic pachymeningitis; Immunoglobulin G4 related disease; Immunoglobulin G4 related hypertrophic pachymeningitis.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, Fukushima M, Nikaido T, Nakayama K, Usuda N, Kiyosawa K. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:732–738. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi H, Yamamoto M, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Shinomura Y, Imai K. The birthday of a new syndrome: IgG4-related diseases constitute a clinical entity. Autoimmun Rev. 2010;9:591–594. - PubMed
-
- Tang H, Ding G, Xiong J, Zhu H, Hua L, Xie Q, Gong Y. Clivus Inflammatory Pseudotumor Associated with Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease. World Neurosurg. 2018;118:71–74. - PubMed
-
- Cha YJ, Lee SK, Chang JH, Kim SH. Report of a rare case of atypical lymphoplasmacyte-rich meningioma in the tentorium mimicking idiopathic hypertrophic pachymeningitis. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2016;33:216–221. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

