Nafamostat mesylate prevents metastasis and dissemination of neuroblastoma through vascular endothelial growth factor inhibition
- PMID: 35949892
- PMCID: PMC9353881
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2022.2571
Nafamostat mesylate prevents metastasis and dissemination of neuroblastoma through vascular endothelial growth factor inhibition
Abstract
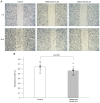
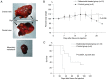
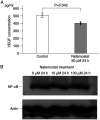
Neuroblastoma is a highly malignant disease with a poor prognosis and few treatment options. Despite conventional chemotherapy for neuroblastoma, resistance, invasiveness, and metastatic mobility limit the treatment efficacy. Therefore, it is necessary to develop new strategies for treating neuroblastoma. The present study aimed to evaluate the anticancer effects of nafamostat mesylate, a previously known serine protease inhibitor, on neuroblastoma cells. Effects of nafamostat mesylate on neuroblastoma cell migration and proliferation were analyzed by wound healing assay and WST-8 assay, respectively. To elucidate the mechanisms underlying the effects of nafamostat mesylate on neuroblastoma, the expression levels of NF-κB were measured via western blotting, and the production of the cytokine vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the cell culture supernatants was determined via ELISA. In addition, a mouse model of hematogenous metastasis was used to investigate the effects of nafamostat mesylate on neuroblastoma. It was determined that nafamostat mesylate significantly inhibited migration and invasion of Neuro-2a cells, but it had no effect on cell proliferation at 24 h after treatment. Exposure of Neuro-2a cells to nafamostat mesylate resulted in decreased vascular endothelial growth factor production, which could be a pivotal mechanism underlying the inhibitory effects of neuroblastoma metastasis. The results of the present study suggest that nafamostat mesylate may be an effective treatment against neuroblastoma invasion and metastasis.
Keywords: metastasis; murine model; nafamostat mesylate; neuroblastoma; vascular endothelial growth factor.
Copyright: © Morimoto et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nafamostat mesilate can prevent adhesion, invasion and peritoneal dissemination of pancreatic cancer thorough nuclear factor kappa-B inhibition.J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2011 Sep;18(5):731-9. doi: 10.1007/s00534-011-0390-9. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2011. PMID: 21484229
-
Nafamostat mesylate decreases skin flap necrosis in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes by protecting the endothelial glycocalyx.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 May 28;710:149843. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.149843. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38593617
-
Delayed administration of nafamostat mesylate inhibits thrombin-mediated blood-spinal cord barrier breakdown during acute spinal cord injury in rats.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Jul 16;19(1):189. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02531-w. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 35842640 Free PMC article.
-
Nafamostat mesylate attenuates the pathophysiologic sequelae of neurovascular ischemia.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Dec;15(12):2217-2234. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.284981. Neural Regen Res. 2020. Retraction in: Neural Regen Res. 2022 May;17(5):958. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.295353. PMID: 32594033 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
The Molecular Aspect of Antitumor Effects of Protease Inhibitor Nafamostat Mesylate and Its Role in Potential Clinical Applications.Front Oncol. 2019 Sep 3;9:852. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00852. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31552177 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
