Application of PD-L1 blockade in refractory histiocytic sarcoma: A case report
- PMID: 35949894
- PMCID: PMC9353867
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2022.2569
Application of PD-L1 blockade in refractory histiocytic sarcoma: A case report
Abstract
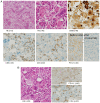
Histiocytic sarcoma (HS) is a rare hematological malignancy, which exhibits morphological and immunophenotypic features of histiocytes. A standard therapy for HS has not yet been established due to its rareness; therefore, disease control is not always possible. A multimodal treatment strategy has been suggested for HS. The present study reported on a case of a 43-year-old female patient who complained of left femoral pain, which was caused by left femoral bone mass. A biopsy of their left femoral bone tumor revealed that the patient had HS. Their sarcoma was localized in the femoral bone and was not considered to be curable, due to local infiltration of the bone tumor beyond the periosteum. The patient then underwent two types of HS-specific chemotherapy; however, both regimens were ineffective. As a result, they underwent radiation therapy at the sites of progressive disease. Because the HS cells of the patient expressed PD-L1, they were treated with nivolumab (240 mg/body, biweekly) for residual diseases in the right occipital bone, multiple lung nodules, intrapelvic right lymph node and primary site. Nivolumab treatment resulted in a complete response at all sites, with the exception of the primary site, which was confirmed by 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography. The patient received additional nivolumab treatment as consolidation therapy for 1 year. In addition, residual disease of the femoral head was completely resected. The surgically resected refractory tumor revealed the tumor cells no longer pathologically expressed PD-L1 . In conclusion, for refractory and recurrent HS in which surgical resection is not appropriate, treatment with immune-checkpoint inhibitors, such as nivolumab, may be considered an optional but promising immunotherapy if the tumor histologically expresses PD-L1. The present study detected one of the refractory mechanisms of ICI treatment.
Keywords: 18F-FDG-PET; PD-L1; histiocytic sarcoma; immune-checkpoint inhibitor; nivolumab; resistance mechanism.
Copyright: © Imataki et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thiele J. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Revised Fourth Edition World Health Organization classification of tumours. IARC, Lyon, 2017.
-
- Emile JF, Abla O, Fraitag S, Horne A, Haroche J, Donadieu J, Requena-Caballero L, Jordan MB, Abdel-Wahab O, Allen CE, et al. Revised classification of histiocytoses and neoplasms of the macrophage-dendritic cell lineages. Blood. 2016;127:2672–2681. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-01-690636. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
