Hypernatremia in Newborns: A Practical Approach to Management
- PMID: 35950014
- PMCID: PMC9247442
- DOI: 10.1159/000524637
Hypernatremia in Newborns: A Practical Approach to Management
Abstract
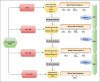
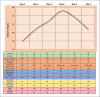
Hypernatremia is a potentially serious condition in both term and preterm babies, which can lead to severe and permanent neurological damage. There are many physiological changes in sodium homeostasis that occur soon after birth. Understanding this physiological process, early anticipation of hypernatremia and familiarization with the neonatal management of hypernatremia can prevent mortality and long-term morbidity associated with this condition. This review aims to provide a practical and understandable approach to the diagnosis and management of hypernatremia in neonates.
Keywords: Dehydration; Neonate; Preterm; Sodium.
Copyright © 2022 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Adrogué HJ, Madias NE. Hypernatremia. N Engl J Med. 2000 May 18;342((20)):1493–9. - PubMed
-
- Boskabadi H, Maamouri G, Ebrahimi M, Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Esmaeily H, Sahebkar A, et al. Neonatal hypernatremia and dehydration in infants receiving inadequate breastfeeding. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2010;19((3)):301–7. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan JA, Siegler RW, Schmunk GA. Fatal hypernatremic dehydration in exclusively breast-fed newborn infants due to maternal lactation failure. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 1998 Mar;19((1)):19–22. - PubMed
-
- van Amerongen RH, Moretta AC, Gaeta TJ. Severe hypernatremic dehydration and death in a breast-fed infant. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2001 Jun;17((3)):175–80. - PubMed
-
- Unal S, Arhan E, Kara N, Uncu N, Aliefendioğlu D. Breast-feeding-associated hypernatremia: retrospective analysis of 169 term newborns. Pediatr Int. 2008 Feb;50((1)):29–34. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

