Macrophage polarization as a potential therapeutic target for atherosclerosis: a dynamic stochastic modelling study
- PMID: 35950200
- PMCID: PMC9346359
- DOI: 10.1098/rsos.220239
Macrophage polarization as a potential therapeutic target for atherosclerosis: a dynamic stochastic modelling study
Abstract
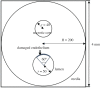
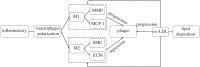
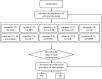
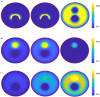
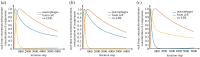
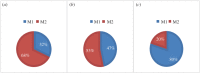
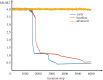
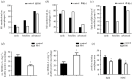
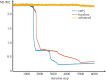
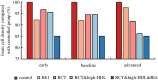
We proposed a dynamic stochastic mathematical model to evaluate the role of macrophage polarization in plaque development. The dynamic process of macrophages from proliferation to death was simulated under different lipid microenvironments. The probability of macrophage phenotypic switching was described using a Bernoulli distribution where the stochastic variable was determined by the local lipid level. Moreover, the interactions between macrophages and microenvironmental factors vary with macrophage phenotype. We investigated the distribution of key microenvironmental factors, the dynamics of macrophage polarization and its influence on foam cell formation. M1 macrophages were found to predominate in advanced plaque corresponding to the exacerbated inflammation observed in mice experiments. The imbalance between the deposition of oxidized low-density lipoprotein and phagocytic effects of macrophages governed the formation of foam cells. Furthermore, we simulated targeted therapies by either directly inhibiting the polarization probability to M1 macrophages or indirectly regulating macrophage polarization due to high-density lipoprotein levels. Comparison of simulation results with experimental findings in both therapies indicated that the intervention and regulation of macrophage polarization could influence plaque microenvironment and subsequently induce plaque regression, especially in the early stage. The proposed modelling system can facilitate the evaluation of novel therapies targeting macrophage polarization.
Keywords: macrophages; polarization; target therapy.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Huang-Lian-Jie-Du Decoction Attenuates Atherosclerosis and Increases Plaque Stability in High-Fat Diet-Induced ApoE-/- Mice by Inhibiting M1 Macrophage Polarization and Promoting M2 Macrophage Polarization.Front Physiol. 2021 Sep 2;12:666449. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.666449. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34539422 Free PMC article.
-
Role of KCa3.1 Channels in Macrophage Polarization and Its Relevance in Atherosclerotic Plaque Instability.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Feb;37(2):226-236. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308461. Epub 2016 Dec 29. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28062499
-
Ginsenoside Rb2 Alleviated Atherosclerosis by Inhibiting M1 Macrophages Polarization Induced by MicroRNA-216a.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 3;12:764130. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.764130. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35046806 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin as a potential modulator of M1 and M2 macrophages: new insights in atherosclerosis therapy.Heart Fail Rev. 2019 May;24(3):399-409. doi: 10.1007/s10741-018-09764-z. Heart Fail Rev. 2019. PMID: 30673930 Review.
-
Macrophage Subsets and Death Are Responsible for Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 30;13:843712. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.843712. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35432323 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Blood Lipoproteins Shape the Phenotype and Lipid Content of Early Atherosclerotic Lesion Macrophages: A Dual-Structured Mathematical Model.Bull Math Biol. 2024 Aug 2;86(9):112. doi: 10.1007/s11538-024-01342-9. Bull Math Biol. 2024. PMID: 39093509 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of mtDNA Mutations in Atherosclerosis: The Influence of Mitochondrial Dysfunction on Macrophage Polarization.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 25;26(3):1019. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031019. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940788 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

