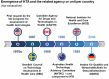
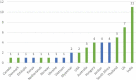
How Least Developed to Lower-Middle Income Countries Use Health Technology Assessment: A Scoping Review
- PMID: 35950264
- PMCID: PMC9970250
- DOI: 10.1080/20477724.2022.2106108
How Least Developed to Lower-Middle Income Countries Use Health Technology Assessment: A Scoping Review
Abstract
Health Technology Assessment (HTA) is a multidisciplinary tool to inform healthcare decision-making. HTA has been implemented in high-income countries (HIC) for several decades but has only recently seen a growing investment in low- and middle-income countries. A scoping review was undertaken to define and compare the role of HTA in least developed and lower middle-income countries (LLMIC). MEDLINE and EMBASE databases were searched from January 2015 to August 2021. A matrix comprising categories on HTA objectives, methods, geographies, and partnerships was used for data extraction and synthesis to present our findings. The review identified 50 relevant articles. The matrix was populated and sub-divided into further categories as appropriate. We highlight topical aspects of HTA, including initiatives to overcome well-documented challenges around data and capacity development, and identify gaps in the research for consideration. Those areas we found to be under-studied or under-utilized included disinvestment, early HTA/implementation, system-level interventions, and cross-sectoral partnerships. We consider broad practical implications for decision-makers and researchers aiming to achieve greater interconnectedness between HTA and health systems and generate recommendations that LLMIC can use for HTA implementation. Whilst HIC may have led the way, LLMIC are increasingly beginning to develop HTA processes to assist in their healthcare decision-making. This review provides a forward-looking model that LLMIC can point to as a reference for their own implementation. We hope this can be seen as timely and useful contributions to optimize the impact of HTA in an era of investment and expansion and to encourage debate and implementation.
Keywords: Decision making; Health Technology Assessment; Low and Middle Income Countries.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Luz A, Santatiwongchai B, Pattanaphesaj J, et al. Identifying priority methodological issues in economic evaluation in low- and middle-income countries: finding the holy grail. http://gear4healthcom/gear. 2017. - PMC - PubMed
-
- O’Rourke B, Oortwijn W, Schuller T.. The new definition of health technology assessment: a milestone in international collaboration. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2020;36(1):1–4. - PubMed
-
- Glassman A, Giedion U, Smith PC. What’s in, what’s out: designing benefits for universal health coverage. Washington DC: Center for Global Development; 2017.
-
- Grieve E, Hesselgreaves H, Wu O, et al. The Value of Health Technology Assessment: a mixed methods framework [version 1; not peer reviewed]. F1000res 2017, 6:2171 (document) 10.7490/f1000research.1115169.1 - DOI
-
- Stevens AJ, Longson C. At the center of health care policy making: the use of health technology assessment at NICE. Med Decis Mak. 2013;33(3):320–324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources