Hippocampal fear engrams modulate ethanol-induced maladaptive contextual generalization in mice
- PMID: 35950345
- PMCID: PMC11964089
- DOI: 10.1002/hipo.23463
Hippocampal fear engrams modulate ethanol-induced maladaptive contextual generalization in mice
Abstract
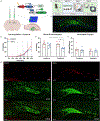
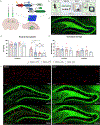
The compounding symptomatology of alcohol use disorder (AUD) and co-occurring mental health disorders gives rise to interactions of maladaptive neurobiological processes, the etiology of which are elusive. Here, we devised an optogenetic strategy aimed at rescuing maladaptive fear processing in male c57BL/6 mice that underwent a chronic ethanol administration and forced abstinence paradigm. In the first experiment, we confirmed that fear acquisition and maladaptive contextual generalization was potentiated in ethanol-exposed mice during fear conditioning and exposure to a novel environment, respectively. In the second experiment, using an activity-dependent tet-tag system, we labeled the neural ensemble selectively activated by contextual fear conditioning in the dorsal hippocampus with an inhibitory opsin to attenuate behavioral dysfunctions resulting from ethanol exposure. We found that acute optogenetic perturbations during exposure to a novel environment suppressed maladaptive generalization in ethanol-exposed mice. These results provide further evidence for a crucial link between ethanol exposure and impaired fear memory processing by providing cellular and behavioral insights into the neural circuitry underlying AUD and maladaptive fear processing.
Keywords: addiction; alcohol; engram; fear conditioning; generalization; hippocampus; optogenetics; withdrawal.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chronic activation of fear engrams induces extinction-like behavior in ethanol-exposed mice.Hippocampus. 2021 Jan;31(1):3-10. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23263. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Hippocampus. 2021. PMID: 32946184 Free PMC article.
-
Dominant activities of fear engram cells in the dorsal dentate gyrus underlie fear generalization in mice.PLoS Biol. 2024 Jul 12;22(7):e3002679. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002679. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 38995985 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific deficits in biochemical but not behavioral responses to delay fear conditioning in prenatal alcohol exposure mice.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018 Dec;156:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2018. PMID: 30316893 Free PMC article.
-
Acute ethanol withdrawal impairs contextual learning and enhances cued learning.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015 Feb;39(2):282-90. doi: 10.1111/acer.12614. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015. PMID: 25684050 Free PMC article.
-
Inception of a false memory by optogenetic manipulation of a hippocampal memory engram.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 Dec 2;369(1633):20130142. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0142. Print 2014 Jan 5. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24298144 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

