Remote blood pressure monitoring with a wearable photoplethysmographic device in patients undergoing coronary angiography: the senbiosys substudy
- PMID: 35950543
- PMCID: PMC9632946
- DOI: 10.1097/MBP.0000000000000615
Remote blood pressure monitoring with a wearable photoplethysmographic device in patients undergoing coronary angiography: the senbiosys substudy
Abstract
Aims: The purpose of this study is to evaluate the accuracy of the Senbiosys device in measuring blood pressure (BP) by photoplethysmography (PPG) in patients undergoing coronary angiography.
Methods: This is a substudy within the Senbiosys trial, which is a prospective, single-arm, single-center study, evaluating the accuracy of BP estimation of the Senbiosys device compared to invasive BP. Patients referred for coronary angiography underwent invasive BP measurement and simultaneously wore the Senbiosys ring. SBP and DBP estimations measured by the Senbiosys device were compared with invasive measurements.
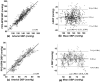
Results: A total of 25 patients were included. Overall, 708 epochs with adequate PPG signal belonging to 17 patients were analyzed. A total of 84% of the SBP estimates and 99% of the DBP estimates have an absolute error of less than 10 mmHg compared with the invasive measurements. Mean difference was 2.3 ± 7.0 mmHg and 0.5 ± 3.5 mmHg for SBP and DBP, respectively.
Conclusion: The Senbiosys device is accurate enough to determine BP in a selected population undergoing coronary angiography.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
A.C. is the cofounder and CTO of Senbiosys. A.B. is the cofounder and CSO of Senbiosys. S.H. is a system engineer at Senbiosys. The Swiss company Senbiosys SA is a nonprofit company that produces PPG sensors (
Figures

References
-
- Caizzone A. An ultra low-noise micropower PPG sensor. 2021.
-
- Teng XF, Zhang YT. Continuous and noninvasive estimation of arterial blood pressure using a photoplethysmographic approach. In: Proceedings of the 25th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, vol. 4; 2003. pp. 3153–3156.
-
- Choudhury AD, Banerjee R, Sinha A, Kundu S. Estimating blood pressure using Windkessel model on photoplethysmogram. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2014; 2014:4567–4570. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

