Maternal high-fat diet modifies epigenetic marks H3K27me3 and H3K27ac in bone to regulate offspring osteoblastogenesis in mice
- PMID: 35950595
- PMCID: PMC9665156
- DOI: 10.1080/15592294.2022.2111759
Maternal high-fat diet modifies epigenetic marks H3K27me3 and H3K27ac in bone to regulate offspring osteoblastogenesis in mice
Abstract
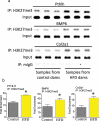
Studies from both humans and animal models indicated that maternal chronic poor-quality diet, especially a high fat diet (HFD), is significantly associated with reduced bone density and childhood fractures in offspring. When previously studied in a rat model, our data suggested that maternal HFD changes epigenetic marks such as DNA methylation and histone modifications to control osteoblast metabolism. In mouse embryonic and postnatal offspring bone samples, a ChIP-sequencing (ChIP-Seq)-based genome-wide method was used to locate the repressive histone mark H3K27me3 (mediated via the polycomb histone methyltransferase, Ezh2) and expressive histone mark H3K27ac (p300/CBP mediated) throughout the genome. Using isolated mouse embryonic cells from foetal calvaria (osteoblast-like cells), H3K27me3 ChIP-Seq showed that 147 gene bodies and 26 gene promoters in HFD embryotic samples had a greater than twofold increase in H3K27me peaks compared to controls. Among the HFD samples, Pthlh and Col2a1 that are important genes playing roles during chondro- and osteogenesis had significantly enriched levels of H3K27me3. Their decreased mRNA expression was confirmed by real-time PCR and standard ChIP analysis, indicating a strong association with Ezh2 mediated H3K27me3 epigenetic changes. Using embryonic calvaria osteoblastic cells and offspring bone samples, H3K27ac ChIP-Seq analysis showed that osteoblast inhibitor genes Tnfaip3 and Twist1 had significantly enriched peaks of H3K27ac in HFD samples compared to controls. Their increased gene expression and association with H3K27ac were also confirmed by real-time PCR and standard ChIP analysis. These findings indicate that chronic maternal HFD changes histone trimethylation and acetylation epigenetic marks to regulate expression of genes controlling osteoblastogenesis.
Keywords: High fat diet; histone modification; maternal obesity; osteoblast.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures






Similar articles
-
Genome-wide profiling of histone H3K27 acetylation featured fatty acid signalling in pancreatic beta cells in diet-induced obesity in mice.Diabetologia. 2018 Dec;61(12):2608-2620. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4735-7. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 30284014
-
Maternal regulation of SATB2 in osteo-progeniters impairs skeletal development in offspring.FASEB J. 2020 Feb;34(2):2511-2523. doi: 10.1096/fj.201901901R. Epub 2019 Dec 23. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 31908011
-
Epigenetic association study uncovered H3K27 acetylation enhancers and dysregulated genes in high-fat-diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in rats.Epigenomics. 2022 Dec;14(23):1523-1540. doi: 10.2217/epi-2022-0362. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Epigenomics. 2022. PMID: 36851897
-
Genomic occupancy of the transcriptional co-activators p300 and CBP.Transcription. 2013 Jan-Feb;4(1):18-23. doi: 10.4161/trns.22601. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Transcription. 2013. PMID: 23131664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics in the Uterine Environment: How Maternal Diet and ART May Influence the Epigenome in the Offspring with Long-Term Health Consequences.Genes (Basel). 2021 Dec 23;13(1):31. doi: 10.3390/genes13010031. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052371 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in research regarding epithelial-mesenchymal transition and prostate cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 May 30;13:1583255. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1583255. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40519259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Rendition of Adipose Genes Under Epigenetic Regulation: Revealing New Mechanisms of Obesity Occurrence.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Jul 11;47(7):540. doi: 10.3390/cimb47070540. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40729009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The P300-ARRDC3 axis participates in maternal subclinical hypothyroidism and is involved in abnormal hepatic insulin sensitivity in adult offspring.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 11;10(21):e39259. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39259. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39568856 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Environmental and Epigenetic Changes on Mesenchymal Stem Cells during Aging.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 30;24(7):6499. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076499. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047469 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cole ZA, Gale CR, Javaid MK, et al. Maternal dietary patterns during pregnancy and childhood bone mass: a longitudinal study. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(4):663–668. - PubMed
-
- Liang C, Oest ME, Jones JC, et al. Gestational high saturated fat diet alters C57BL/6 mouse perinatal skeletal formation. Birth Defects Res B. 2009;86(5):362–369. - PubMed
-
- Chen JR, Zhang J, Lazarenko OP, et al. Inhibition of fetal bone development through epigenetic down-regulation of HoxA10 in obese rats fed high-fat diet. FASEB J. 2012;26(3):1131–1141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
