Regulated cell death in cancer: from pathogenesis to treatment
- PMID: 35950752
- PMCID: PMC10129203
- DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002239
Regulated cell death in cancer: from pathogenesis to treatment
Abstract
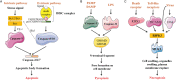
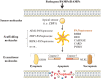
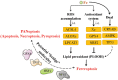
Regulated cell death (RCD), including apoptosis, pyroptosis, necroptosis, and ferroptosis, is regulated by a series of evolutionarily conserved pathways, and is required for development and tissue homeostasis. Based on previous genetic and biochemical explorations of cell death subroutines, the characteristics of each are generally considered distinctive. However, recent in-depth studies noted the presence of crosstalk between the different forms of RCD; hence, the concept of PANoptosis appeared. Cancer, a complex genetic disease, is characterized by stepwise deregulation of cell apoptosis and proliferation, with significant morbidity and mortality globally. At present, studies on the different RCD pathways, as well as the intricate relationships between different cell death subroutines, mainly focus on infectious diseases, and their roles in cancer remain unclear. As cancers are characterized by dysregulated cell death and inflammatory responses, most current treatment strategies aim to selectively induce cell death via different RCD pathways in cancer cells. In this review, we describe five types of RCD pathways in detail with respect to tumorigenesis and cancer progression. The potential value of some of these key effector molecules in tumor diagnosis and therapeutic response has also been raised. We then review and highlight recent progress in cancer treatment based on PANoptosis and ferroptosis induced by small-molecule compounds, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and nanoparticles. Together, these findings may provide meaningful evidence to fill in the gaps between cancer pathogenesis and RCD pathways to develop better cancer therapeutic strategies.
Copyright © 2022 The Chinese Medical Association, produced by Wolters Kluwer, Inc. under the CC-BY-NC-ND license.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018; 68:394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D. Broadening horizons: the role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2021; 18:280–296. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-00462-0. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000; 100:57–70. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81683-9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

