D-Dimer as a Sensitive Biomarker of Survival Rate in Patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 35950823
- PMCID: PMC9797773
- DOI: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2022.21145
D-Dimer as a Sensitive Biomarker of Survival Rate in Patients with COVID-19
Abstract
Objective: The global case fatality rate of coronavirus disease 2019 is 2.16% as announced by the World Health Organization. In Indonesia, according to the Ministry of Health, the number is even higher, reaching a 2.8% case fatality rate. D-dimer levels were found to affect coronavirus disease 2019 patient's survival in several studies. The study aimed to determine whether the amount of D-dimer predicted survival in coronavirus disease 2019 patients.
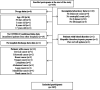
Materials and methods: This research was performed in a retrospective cohort design and used survival analysis. From March 1, 2020, to August 31, 2020, the samples were collected from polymerase chain reaction-confirmed coronavirus disease 2019 patients at Mohammad Hoesin General Hospital in Palembang, South Sumatera, Indonesia. We used electronic medical records to obtain demographic (age and gender), coexisting condition, laboratory (coagulation and hematologic test), and outcome (non-survivors or survivors) data. The chi-square and Mann-Whitney tests were used to evaluate the results. The Kaplan-Meier method and the Mantel-Haenszel log-rank test were used to examine D-dimer levels and patient outcomes. Youden index was calculated to determine the optimal cut-off value of D-dimer.
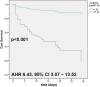
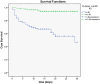
Results: There were 52 non-survivors and 235 survivors among the 287 patients who met the inclusion criterion. Non-survivors had D-dimer levels of more than 1.49 mg/L in 82.69%of cases. Males had lower cut-off compared to females (>1.49 mg/L vs. >2.2 mg/L). The researchers discovered a highly significant correlation between D-dimer levels and coronavirus disease 2019 mortality (P=.001). The c-index analysis showed that D-dimer (0.79, 95% CI: 0.73-0.83) ability for mortality prediction was the second-best compared with other laboratory markers.
Conclusion: D-dimer can be used as a predictor of coronavirus disease 2019 in-hospital mortality for early identification of coagulopathy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High serum lactate dehydrogenase and dyspnea: Positive predictors of adverse outcome in critical COVID-19 patients in Yichang.World J Clin Cases. 2020 Nov 26;8(22):5535-5546. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i22.5535. World J Clin Cases. 2020. PMID: 33344544 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic changes of D-dimer and neutrophil-lymphocyte count ratio as prognostic biomarkers in COVID-19.Respir Res. 2020 Jul 3;21(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01428-7. Respir Res. 2020. PMID: 32620118 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors Associated With Six-Month Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Single-Institution Study.Cureus. 2022 Nov 7;14(11):e31206. doi: 10.7759/cureus.31206. eCollection 2022 Nov. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36505139 Free PMC article.
-
A novel combined index of D-dimer, fibrinogen, albumin, and platelet (FDAPR) as mortality predictor of COVID-19.Niger J Clin Pract. 2022 Sep;25(9):1418-1423. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_1633_21. Niger J Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 36149199
-
Association of inflammatory biomarker abnormalities with mortality in COVID-19: a meta-analysis.Bull Natl Res Cent. 2022;46(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s42269-022-00733-z. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Bull Natl Res Cent. 2022. PMID: 35261542 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Risk factors associated with fatal thrombosis in hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients on anticoagulant therapy.J Family Community Med. 2023 Oct-Dec;30(4):273-279. doi: 10.4103/jfcm.jfcm_60_23. Epub 2023 Oct 13. J Family Community Med. 2023. PMID: 38044972 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and COVID-19: The Impact of Hematological Biomarkers on Disease Severity and Outcomes.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 17;14(8):2765. doi: 10.3390/jcm14082765. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40283596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on Innate Immunity in Acute Kidney Injury-Lessons Taken from COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 19;23(20):12514. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012514. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD4+ and CD8+ cell counts are significantly correlated with absolute lymphocyte count in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a retrospective study.PeerJ. 2023 Jun 23;11:e15509. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15509. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37377785 Free PMC article.
-
Critical biomarkers in the battle against COVID-19: unveiling thrombotic risks and predictive indicators in Syrian hospitals.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025 Mar 20;87(8):4803-4810. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003168. eCollection 2025 Aug. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40787540 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Penanganan GTP. COVID-19. Peta Sebaran; 2020. Available at: https://covid19.go.id/peta-sebaran. Accessed 2021 Jan 29.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous